MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 SUPPLY TDA4600 (SIEMENS).
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Power supply Description based on TDA4601d (SIEMENS)
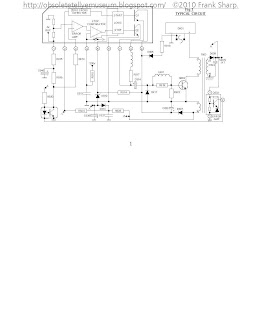
 ring of the output voltage and vice versa, oscillation frequency also varies according to load, the higher the load the lower the frequency etc. should the voltage at pin 3 exceed 2.3v an internal flip flop is triggered causing the chopper drive mark space ratio to extend to 244 (off time) to 1 (on time), the chip is now in over volts trip condition. Pin 4 At this pin a sawtooth waveform is generated which simulates chopper current, it is produced by a time constant network R810 and C813. C813 charges when the chopper is on and is discharged when the chopper is off, by an internal switch strapping pin 4 to the internal +2v reference, see Fig 2. The amplitude of the ramp is proportional to chopper drive. In an overload condition it reaches 4v amplitude at which point chopper drive is reduced to a mark-space ratio of 13 to 1, the chip is then in over current trip. The I.C. can easily withstand a short circuit on the H.T. rail and in such a case the power supply simply squegs quietly. Pin 4 is protected by internal protection components which limit the maximum voltage at this pin to 6.5v. Should a fault occur in either of the time constant components, then the chopper transistor will probably be destroyed. Pin 5 This pin can be used for remote control on/off switching of the power supply, it is normally held at about +7v and will cause the chip to enter standby mode if it falls below 2v. Pin 6 Ground. Pin 7 Chopper switch off pin. This pin clamps the chopper drive voltage to 1.6v in order to switch off the chopper. Pin 8 Chopper base current output drive pin. Pin 9 L.T. pin, approximately 9v under start-up conditions and 16v during normal running, Current consumption of the I.C. is typically 135mA. The voltage at this pin must reach 6.7v in order for the chip to start-up.
ring of the output voltage and vice versa, oscillation frequency also varies according to load, the higher the load the lower the frequency etc. should the voltage at pin 3 exceed 2.3v an internal flip flop is triggered causing the chopper drive mark space ratio to extend to 244 (off time) to 1 (on time), the chip is now in over volts trip condition. Pin 4 At this pin a sawtooth waveform is generated which simulates chopper current, it is produced by a time constant network R810 and C813. C813 charges when the chopper is on and is discharged when the chopper is off, by an internal switch strapping pin 4 to the internal +2v reference, see Fig 2. The amplitude of the ramp is proportional to chopper drive. In an overload condition it reaches 4v amplitude at which point chopper drive is reduced to a mark-space ratio of 13 to 1, the chip is then in over current trip. The I.C. can easily withstand a short circuit on the H.T. rail and in such a case the power supply simply squegs quietly. Pin 4 is protected by internal protection components which limit the maximum voltage at this pin to 6.5v. Should a fault occur in either of the time constant components, then the chopper transistor will probably be destroyed. Pin 5 This pin can be used for remote control on/off switching of the power supply, it is normally held at about +7v and will cause the chip to enter standby mode if it falls below 2v. Pin 6 Ground. Pin 7 Chopper switch off pin. This pin clamps the chopper drive voltage to 1.6v in order to switch off the chopper. Pin 8 Chopper base current output drive pin. Pin 9 L.T. pin, approximately 9v under start-up conditions and 16v during normal running, Current consumption of the I.C. is typically 135mA. The voltage at this pin must reach 6.7v in order for the chip to start-up. Semiconductor
circuit for supplying power to electrical equipment, comprising a
transformer having a primary winding connected, via a parallel
connection of a collector-emitter path of a transistor with a first
capacitor, to both outputs of a rectifier circuit supplied, in turn, by a
line a-c voltage; said transistor having a base controlled via a second
capacitor by an output of a control circuit acted upon, in turn by the
rectified a-c line voltage as actual value and by a reference voltage;
said transformer having a first secondary winding to which the
electrical equipment to be supplied is connected; said transformer
having a second secondary winding with one terminal thereof connected to
the emitter of said transistor and the other terminal thereof connected
to an anode of a first diode leading to said control circuit; said
transformer having a third secondary winding with one terminal thereof
connected, on the one hand, via a series connection of a third capacitor
with a first resistance, to the other terminal of said third secondary
winding and connected, on the other hand, to the emitter of said
transistor, the collector of which is connected to said primary winding;
a point between said third capacitor and said first resistance being
connected to the cathode of a second diode; said control circuit having
nine terminals including a first terminal delivering a reference voltage
and connected, via a voltage divider formed of a third and fourth
series-connected resistances, to the anode of said second diode; a
second terminal of said control circuit serving for zero-crossing
identification being connected via a fifth resistance to said cathode of
said second diode; a third terminal of said control-circuit serving as
actual value input being directly connected to a divider point of said
voltage divider forming said connection of said first terminal of said
control circuit to said anode of said second diode; a fourth terminal of
said control circuit delivering a sawtooth voltage being connected via a
sixth resistance to a terminal of said primary winding of said
transformer facing away from said transistor; a fifth terminal of said
control circuit serving as a protective input being connected, via a
seventh resistance to the cathode of said first diode and, through the
intermediary of said seventh resistance and an eighth resistance, to the
cathode of a third diode having an anode connected to an input of said
rectifier circuit; a sixth terminal of said control circuit carrying
said reference potential and being connected via a fourth capacitor to
said fourth terminal of said control circuit and via a fifth capacitor
to the anode of said second diode; a seventh terminal
of said control circuit establishing a potential for pulses controlling
said transistor being connected directly and an eighth terminal of said
control circuit effecting pulse control of the base of said transistor
being connected through the intermediary of a ninth resistance to said
first capacitor leading to the base of said transistor; and a ninth
terminal of said control circuit serving as a power supply input of said
control circuit being connected both to the cathode of said first diode
as well as via the intermediary of a sixth capacitor to a terminal of
said second secondary winding as well as to a terminal of said third
secondary winding.
Semiconductor
circuit for supplying power to electrical equipment, comprising a
transformer having a primary winding connected, via a parallel
connection of a collector-emitter path of a transistor with a first
capacitor, to both outputs of a rectifier circuit supplied, in turn, by a
line a-c voltage; said transistor having a base controlled via a second
capacitor by an output of a control circuit acted upon, in turn by the
rectified a-c line voltage as actual value and by a reference voltage;
said transformer having a first secondary winding to which the
electrical equipment to be supplied is connected; said transformer
having a second secondary winding with one terminal thereof connected to
the emitter of said transistor and the other terminal thereof connected
to an anode of a first diode leading to said control circuit; said
transformer having a third secondary winding with one terminal thereof
connected, on the one hand, via a series connection of a third capacitor
with a first resistance, to the other terminal of said third secondary
winding and connected, on the other hand, to the emitter of said
transistor, the collector of which is connected to said primary winding;
a point between said third capacitor and said first resistance being
connected to the cathode of a second diode; said control circuit having
nine terminals including a first terminal delivering a reference voltage
and connected, via a voltage divider formed of a third and fourth
series-connected resistances, to the anode of said second diode; a
second terminal of said control circuit serving for zero-crossing
identification being connected via a fifth resistance to said cathode of
said second diode; a third terminal of said control-circuit serving as
actual value input being directly connected to a divider point of said
voltage divider forming said connection of said first terminal of said
control circuit to said anode of said second diode; a fourth terminal of
said control circuit delivering a sawtooth voltage being connected via a
sixth resistance to a terminal of said primary winding of said
transformer facing away from said transistor; a fifth terminal of said
control circuit serving as a protective input being connected, via a
seventh resistance to the cathode of said first diode and, through the
intermediary of said seventh resistance and an eighth resistance, to the
cathode of a third diode having an anode connected to an input of said
rectifier circuit; a sixth terminal of said control circuit carrying
said reference potential and being connected via a fourth capacitor to
said fourth terminal of said control circuit and via a fifth capacitor
to the anode of said second diode; a seventh terminal
of said control circuit establishing a potential for pulses controlling
said transistor being connected directly and an eighth terminal of said
control circuit effecting pulse control of the base of said transistor
being connected through the intermediary of a ninth resistance to said
first capacitor leading to the base of said transistor; and a ninth
terminal of said control circuit serving as a power supply input of said
control circuit being connected both to the cathode of said first diode
as well as via the intermediary of a sixth capacitor to a terminal of
said second secondary winding as well as to a terminal of said third
secondary winding.Description:
 Such a blocking oscillator switching
power supply is described in the German periodical, "Funkschau" (1975)
No. 5, pages 40 to 44. It is well known that the purpose of such a
circuit is to supply electronic equipment, for example, a television
set, with stabilized and controlled supply voltages. Essential for such
switching power supply is a power switching transistor i.e. a bipolar
transistor with high switching speed and high reverse voltage. This
transistor therefore constitutes an important component of the control
element of the control circuit. Furthermore, a high operating frequency
and a transformer intended for a high operating frequency are provided,
because generally, a thorough separation of the equipment to be supplied
from the supply naturally is desired. Such switching power supplies may
be constructed either for synchronized or externally controlled
operation or for non-synchronized or free-running operation. A blocking
converter is understood to be a switching power supply in which power is
delivered to the equipment to be supplied only if the switching
transistor establishing the connection between the primary coil of the
transformer and the rectified a-c voltage is cut off. The power
delivered by the line rectifier to the primary coil of the transformer
while the switching transistor is open, is interim-stored in the
transformer and then delivered to the consumer on the secondary side of
the transformer with the switching transistor cut off.
Such a blocking oscillator switching
power supply is described in the German periodical, "Funkschau" (1975)
No. 5, pages 40 to 44. It is well known that the purpose of such a
circuit is to supply electronic equipment, for example, a television
set, with stabilized and controlled supply voltages. Essential for such
switching power supply is a power switching transistor i.e. a bipolar
transistor with high switching speed and high reverse voltage. This
transistor therefore constitutes an important component of the control
element of the control circuit. Furthermore, a high operating frequency
and a transformer intended for a high operating frequency are provided,
because generally, a thorough separation of the equipment to be supplied
from the supply naturally is desired. Such switching power supplies may
be constructed either for synchronized or externally controlled
operation or for non-synchronized or free-running operation. A blocking
converter is understood to be a switching power supply in which power is
delivered to the equipment to be supplied only if the switching
transistor establishing the connection between the primary coil of the
transformer and the rectified a-c voltage is cut off. The power
delivered by the line rectifier to the primary coil of the transformer
while the switching transistor is open, is interim-stored in the
transformer and then delivered to the consumer on the secondary side of
the transformer with the switching transistor cut off. In the blocking converter described in the aforementioned reference in the literature, "Funkschau" (1975), No. 5, Pages 40 to 44, the power switching transistor is connected in the manner defined in the introduction to this application. In addition, a so-called starting circuit is provided. Because several diodes are generally provided in the overall circuit of a blocking oscillator according to the definition provided in the introduction hereto, it is necessary, in order not to damage these diodes, that due to the collector peak current in the case of a short circuit, no excessive stress of these diodes and possibly existing further sensitive circuit parts can occur.
 Considering
the operation of a blocking oscillator, this means that, in the event of
a short circuit, the number of collector current pulses per unit time
must be reduced. For this purpose, a control and regulating circuit is provided.
Simultaneously, a starting circuit must bring the blocking converter
back to normal operation when the equipment is switched on, and after
disturbances, for example, in the event of a short circuit. The starting
circuit shown in the literature reference "Funkschau" on Page 42
thereof, differs to some extent already from the conventional d-c
starting circuits. It is commonly known for all heretofore known
blocking oscillator circuits, however, that a thyristor or an equivalent
circuit replacing the thyristor is essential for the operation of the
control circuit.
Considering
the operation of a blocking oscillator, this means that, in the event of
a short circuit, the number of collector current pulses per unit time
must be reduced. For this purpose, a control and regulating circuit is provided.
Simultaneously, a starting circuit must bring the blocking converter
back to normal operation when the equipment is switched on, and after
disturbances, for example, in the event of a short circuit. The starting
circuit shown in the literature reference "Funkschau" on Page 42
thereof, differs to some extent already from the conventional d-c
starting circuits. It is commonly known for all heretofore known
blocking oscillator circuits, however, that a thyristor or an equivalent
circuit replacing the thyristor is essential for the operation of the
control circuit. It is accordingly an object of the invention to provide another starting circuit. It is a further object of the invention to provide a possible circuit for the control circuit which is particularly well suited for this purpose. It is yet another object of the invention to provide such a power supply which is assured of operation over the entire range of line voltages from 90 to 270 V a-c, while the secondary voltages and secondary load variations between no-load and short circuit are largely constant.
 With the foregoing and other objects in view, there is
provided, in accordance with the invention, a blocking oscillator-type
switching power supply for supplying power to electrical equipment
wherein a primary winding of a transformer, in series with an
emitter-collector path of a first bipolar transistor, is connected to a
d-c voltage obtained by rectification of a line a-c voltage fed-in via
two external supply terminals, a secondary winding of the transformer
being connectible to the electrical equipment for supplying power
thereto, the first bipolar transistor having a base controlled by the
output of a control circuit acted upon, in turn, by the rectified a-c
line voltage as actual value and by a set-point transmitter, and
including a starting circuit for further control of the base of the
first bipolar transistor, including a first diode in the starting
circuit having an anode directly connected to one of the supply
terminals supplied by the a-c line voltage and a cathode connected via a
resistor to an input serving to supply power to the control circuit,
the input being directly connected to a cathode of a second diode, the
second diode having an anode connected to one terminal of another
secondary winding of the transformer, the other secondary winding having
another terminal connected to the emitter of the first bipolar
transmitter.
With the foregoing and other objects in view, there is
provided, in accordance with the invention, a blocking oscillator-type
switching power supply for supplying power to electrical equipment
wherein a primary winding of a transformer, in series with an
emitter-collector path of a first bipolar transistor, is connected to a
d-c voltage obtained by rectification of a line a-c voltage fed-in via
two external supply terminals, a secondary winding of the transformer
being connectible to the electrical equipment for supplying power
thereto, the first bipolar transistor having a base controlled by the
output of a control circuit acted upon, in turn, by the rectified a-c
line voltage as actual value and by a set-point transmitter, and
including a starting circuit for further control of the base of the
first bipolar transistor, including a first diode in the starting
circuit having an anode directly connected to one of the supply
terminals supplied by the a-c line voltage and a cathode connected via a
resistor to an input serving to supply power to the control circuit,
the input being directly connected to a cathode of a second diode, the
second diode having an anode connected to one terminal of another
secondary winding of the transformer, the other secondary winding having
another terminal connected to the emitter of the first bipolar
transmitter.  In
accordance with another feature of the invention, there is provided a
second bipolar transistor having the same conduction type as that of the
first bipolar transistor and connected in the starting circuit with the
base thereof connected to a cathode of a semiconductor diode, the
semiconductor diode having an anode connected to the emitter of the
first bipolar transistor, the second bipolar transistor having a
collector connected via a resistor to a cathode of the first diode in
the starting circuit, and having an emitter connected to the input
serving to supply power to the control circuit and also connected to the
cathode of the second diode which is connected to the other secondary
winding of the transformer.
In
accordance with another feature of the invention, there is provided a
second bipolar transistor having the same conduction type as that of the
first bipolar transistor and connected in the starting circuit with the
base thereof connected to a cathode of a semiconductor diode, the
semiconductor diode having an anode connected to the emitter of the
first bipolar transistor, the second bipolar transistor having a
collector connected via a resistor to a cathode of the first diode in
the starting circuit, and having an emitter connected to the input
serving to supply power to the control circuit and also connected to the
cathode of the second diode which is connected to the other secondary
winding of the transformer. In accordance with a further feature of the invention, the base of the second bipolar transistor is connected to a resistor and via the latter to one pole of a first capacitor, the anode of the first diode being connected to the other pole of the first capacitor.
In accordance with an added feature of the invention, the input serving to supply power to the control circuit is connected via a second capacitor to an output of a line rectifier, the output of the line rectifier being directly connected to the emitter of the first bipolar transistor.
 In accordance with an additional feature of
the invention, the other secondary winding is connected at one end to
the emitter of the first bipolar transistor and to a pole of a third
capacitor, the third capacitor having another pole connected, on the one
hand, via a resistor, to the other end of the other secondary winding
and, on the other hand, to a cathode of a third diode, the third diode
having an anode connected via a potentiometer to an actual value input
of the control circuit and, via a fourth capacitor, to the emitter of
the first bipolar transistor.
In accordance with an additional feature of
the invention, the other secondary winding is connected at one end to
the emitter of the first bipolar transistor and to a pole of a third
capacitor, the third capacitor having another pole connected, on the one
hand, via a resistor, to the other end of the other secondary winding
and, on the other hand, to a cathode of a third diode, the third diode
having an anode connected via a potentiometer to an actual value input
of the control circuit and, via a fourth capacitor, to the emitter of
the first bipolar transistor. In accordance with yet another feature of the invention, the control circuit has a control output connected via a fifth capacitor to the base of the first bipolar transistor for conducting to the latter control pulses generated in the control circuit.
In accordance with a concomitant feature of the invention, there is provided a sixth capacitor shunting the emitter-collector path of the first transistor.
 Other features which are considered as characteristic for the invention are set forth in the appended claim.
Other features which are considered as characteristic for the invention are set forth in the appended claim. Although the invention is illustrated and described herein as embodied in a blocking oscillator type switching power supply, it is nevertheless not intended to be limited to the details shown, since various modifications and structural changes may be made therein without departing from the spirit of the invention and within the scope and range of equivalents of the claims.
PHILIPS TDA373O FREQUENCY DEMODULATOR AND DROP OUT COMPENSATOR FOR VIDEO RECORDERS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA3730 is a monolithic integrated circuit for luminance processing in the playback path of video
recorders. The device incorporates two signal channels, one for the main signal and one for the drop
out signal.
Features
FM preamplifier
Limiter in main and drop out channel
Demodulator in main and drop out channel
Drop out detector with Schmitt—trigger
Electronic switches for FM and video signal controlled by drop out detector
Linear and dynamic video de—emphasis
D.C. reference stabilizer
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Supply voltage (pin 7 and pin 23) Vp = V7’ 23.5’ 25 typ. 10 V
Supply current (pin 7 + pin 23) Ip = I7 + I23 typ. 40 mA
FM input signal (pin 17)
(peakvto-peak value) V17.25(p_p) typ. 100 mV
Video output signal (pin 26)
(peak—to~peak value) V25.5(p_p) typ. 2 V
PACKAGE OUTLINE
28-lead DI L; plastic (SOT117).
 INTEL P8051 8-BIT CONTROL-ORIENTED MICROCONTROLLERS
INTEL P8051 8-BIT CONTROL-ORIENTED MICROCONTROLLERS8031AH18051AH18051AHP
8032N+18052N-I
8751W8751H-8
8751BW8752BI-I
High Performance HMOS Process
Internal Timers/Event Counters
2-Level interrupt Priority Structure
32 1/0 Lines (Four 8-Bit Ports)
64K External Program Memory Space
Security Feature Protects EPROM Parts
Against Software Piracy
Boolean Processor
Bit-Addressable RAM
Programmable Full Duplex Serial
Channel
111 Instructions (64 Single-Cycle)
64K External Data Memory Space
Extended Temperature Range
(–40”C to +85”C)
The MCS@51 controllers are optimized for control applications. Byte-processing and numerical operations on small data structures are facilitated by a va
 riety of fast addressing modes for accessing the internal RAM. Theinstruction set provides a convenient menu of 8-bit arithmetic instructions, including multiply and divide instruc-tions. Extensive on-chip support is provided for one-bit variables as a separate data type, allowing direct bit manipulation and testing in control and logic systems that require Boolean processing.
riety of fast addressing modes for accessing the internal RAM. Theinstruction set provides a convenient menu of 8-bit arithmetic instructions, including multiply and divide instruc-tions. Extensive on-chip support is provided for one-bit variables as a separate data type, allowing direct bit manipulation and testing in control and logic systems that require Boolean processing.The 8751H is an EPROMversion of the 8051AH. It has 4 Kbytes of electrically programmable ROM which can be erased with ultraviolet light. His fully compatible with the 8051AH but incorporates one additional feature: a
Program Memory Security bit that can be used to protect the EPROM against unauthorized readout. The
8751H-8 is identical to the 8751H but only operates up to 8 MHz.
The 8051AHP is identical to the 8051AH with the exception of the Protection Feature. To incorporate this
Protection Feature, program verification has been disabled and external memory accesses have been limited to 4K.
The 8052AH is an enhanced version of the 8051AH. It is backwards compatible with the 8051AH and is
fabricated with HMOS IItechnology. The 8052AH enhancements are listed in the table below.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Vcc: Supply voltage.
Vss: Circuit ground.
Port O:Port Ois an 8-bit open drain bidirectional 1/0
port. As an output port each pin can sink 8 LS TTL
inputs.
Port Opins that have 1‘s written to them float, and in
that state can be used as high-impedance inputs.
Port Ois also the multiplexed low-order address and
data bus during accesses to external Program and
Data Memory. In this application it uses strong inter-
nal pullups when emitting 1‘s and can source and
sink 8 LS TTL inputs.
Port Oalso receives the code bytes during program-
ming of the EPROM parts, and outputs the code
bytes during program verification of the ROM and
EPROM parts. External pullups are required during
program verification.
Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional 1/0 port with
internal pullups, The Port 1 output buffers can sink/
source 4 LS TTL inputs. Port 1 pins that have 1‘s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-
UPS,and in that state can be used as inputs. As
inputs, Port 1 pins that are externally pulled low will
source current (IILon the data sheet) because of the
internal pullups.
Port 1 also receives the low-order address bytes
during programming of the EPROM parts and during
program verification of the ROM and EPROM parts.
In the 8032AH, 8052AH and 8752BH, Port 1 pins
P1.Oand P1.1 also
 serve the T2 and T2EX func-
serve the T2 and T2EX func-tions, respectively.
w
Port 2 emits the high-order address byte during
fetches from external Program Memory and during
accesses to external Data Memory that use 16-bit
addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application it
uses strong internal pullups when emitting 1‘s. Dur-
ing accesses to external Data Memory that use 8-bit
addresses (MOVX @Ri),Port 2 emits the contents of
the P2 Special Function Register.
Port 2 also receives the high-order address bits dur-
ing programming of the EPROM parts and during
program verification of the ROM and EPROM parts.
The protection feature of the 8051AHP causes bits
P2.4 through P2.7 to be forced to O,effectively limit-
ing external Data and Code space to 4K each during
external accesses.
Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional l/O port with
internal pullups. The Port 3 output buffers can sink/
source 4 LS TTL inputs. Port 3 pins that have 1‘s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-
UPS,and in that state can be used as inputs. As
inputs, Port 3 pins that are externally pulled low will
source current (IILon the data sheet) because of the
pullups.
Port 3 also serves the functions of various special
features of the MCS 51 Family, as listed below:
Port
Pin
P3,0
P3.1
P3.2
P3,3
P3.4
P3.5
P3.6
P3.7
Alternative Function
RXD (serial input port)
TXD (serial output port)
INTO(external interrupt O)
INT1 (external interrupt 1)
TO(Timer Oexternal input)
T1 (Timer 1 external input)
WR (external data memory write strobe)
~
(external data memory read strobe)
I
Port
Pin I
Alternative Function
I
P1.0
T2 (Timer/Counter 2 External Input)
P1.1
T2EX (Timer/Counter 2
Capture/Reload Trigger)
Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional l/O port with
internal pullups. The Port 2 output buffers can sink/
source 4 LS TTL inputs. Porl 2 pins that have 1‘s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-
UPS,and in that state can be used as inputs. As
inputs, Port 2 pins that are externally pulled low will
source current (IILon the data sheet) because of the
internal pullups.
RST: Reset input. A high on this pin for two machine
cycles while the oscillator is running resets the de-
vice,
ALE/PROG: Address Latch Enable output pulse for
latching the low byte of the address during accesses
to external memory. This pin is also the program
pulse input (PROG) during programming of the
EPROM parts.
In normal operation ALE is emitted at a constant
rate of 1/6the oscillator frequency, and may be used
for external timing or clocking purposes. Note, how-
ever, that one ALE pulse is skipped during each ac-
cess to external Data Memory.
PSEN: Program Store Enable is the read strobe to
external Program Memory.
When the device is executing code from external
Program Memory, PSEN is activated twice each ma-
chine cycle, except that two PSEN activations are
skipped during each access to external Data Memo-
ry
~/Vpp:
External Access enable ~
must be
strapped to VSSin order to enable any MCS 51 de-
vice to fetch code from external Program memory
locations starting at OOOOHup to FFFFH. ~
must
be strapped to VCCfor internal program execution.
Note, however, that if the Security Bit in the EPROM
devices is programmed, the device will not fetch
code from any location in external Program Memory.
This pin also receives the programming supply volt-
age (VPP)during programming of the EPROM parts.
XTAL1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier.
XTAL2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifi-
er,
OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS
XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respec-
tively, of an inverting amplifier which can be config-
ured for use as an on-chip oscillator, as shown in
Figure 3. Either a quartz crystal or ceramic resonator
may be used.To drive the device from an external clock source,
XTAL1 should be grounded, while XTAL2 is driven,
as shown in Figure 4. There are no requirements on
the duty cycle of the external clock signal, since the
input to the internal clocking circuitry is through a
divide-by-two flip-flop, but minimum and maximum
high and low times specified on the data sheet must
be observed.
EXPRESS Version
The Intel EXPRESSsystem offers enhancements to
the operational specifications of t
 he MCS 51 family
he MCS 51 familyof microcontrollers. These EXPRESS products are
designed to meet the needs of those applications
whose operating requirements exceed commercial
standards.
The EXPRESS program includes the commercial
standard temperature range with burn-in, and an ex-
tended temperature range with or without burn-in.
With the commercial standard temperature range,
operational characteristics are guaranteed over the
temperature range of O“C to + 70”C. With the ex-
tended temperature range option, operational char-
acteristics are guaranteed over a range of –40”C to
+ 85”C.
The optional burn-in is dynamic, for a minimum time
of 160 hours at 125°Cwith VCC = 5.5V * 0.25V,
following guidelines in MIL-STD-883, Method 1015.
Package types and EXPRESSversions are identified
by a one- or two-letter prefix to the part number. The
prefixes are listed in Table 1.
For the extended temperature range option, this
data sheet specifies the parameters which deviate
from their commercial temperature range limits.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Ambient Temperature Under Bias –40”C to + 85°C
Storage Temperature
.
–65°C to + 150°C
Voltage on EA/Vpp Pin to Vss
8751H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–0.5V to + 21.5V
8751BH/6752BH
–0.5V tO + 13.OV
Voltage on Any Other Pinto Vss
.
–0.5V to + 7V
Power Dissipation.
. . ...
1.5W
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 VIDEO2000 Reversable video cassette:
 A reversible video cassette
for portable video devices is described, said cassette having two
housing halves (7, 8), mounted displaceably for changing the distance
between the winding spools. The housing halves are connected to each
other by two flat guide parts (13, 14) arranged in parallel. The two
housing halves are releasably locked by two catch hooks (17, 18)
associated with the guide parts.
A reversible video cassette
for portable video devices is described, said cassette having two
housing halves (7, 8), mounted displaceably for changing the distance
between the winding spools. The housing halves are connected to each
other by two flat guide parts (13, 14) arranged in parallel. The two
housing halves are releasably locked by two catch hooks (17, 18)
associated with the guide parts.1. Video-Wendekassette in Form eines im wesentlichen quaderf·ormigen K·orpers mit zwei darin drehbar gelagerten Wickelspulen f·ur das Magnetband und einer an einer schmalen L·angsfl·ache vorgesehenen ·Offnung mit teilweise zur·uckgesetzter Geh·ausewand zur freiliegenden Magnetbandf·uhrung, wobei die Kassette vorzugsweise aus zwei verriegelbaren im wesentlichen geschlossenen Halbteilen besteht, die zur Ver·anderung des Wickelspulenabstandes sowie zur Vergr·osserung der freiliegenden Magnetbandl·ange verschiebbar gelagert sind, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass die Verbindung der verschiebbaren Kassetten
-Halbteile (7,8) durch zwei flache F·uhrungsteile (13, 14) erfolgt, die in parallel angeordneten F·uhrungsnuten (19, 20), die sich in den beiden ·ausseren schmalen L·angsfl·achen (15, 16) der Geh·ausehalbteile befinden, eingelegt sind, und die Verriegelung der beiden Halbteile durch zwei seitenversetzt den F·uhrungsteilen zugeordnete Sperrhaken (17, 18) erfolgt.
2. Video-Wendekassette nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass die F·uhrungsteile (13, 14) aus schmalen bandartigen Metallstreifen bestehen.
3. Video-Wendekassette nach den Anspr·uchen 1 und 2, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass die F·uhrungsteile aus antimagnetischem Federstahlband bestehen.
4. Video-Wendekassette nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass der aus Kunststoff einst·uckig gefertigte Sperrhaken (17, 18) aus einem Hakenteil (22), einem Lagerauge (23) und einem Verbindungssteg (24) besteht, wobei der Verbindungssteg eine Schr·agfl·ache (27) aufweist.
5. Video-Wendekassette nach den Anspr·uchen 1 und 4, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass der Sperrhaken mittels einer Druckfeder (25) in einer die beiden Kassetten-Geh·ausehalbteile verriegelnden Lage gehalten wird.
6. Video-Wendekassette nach einem der Anspr·uche 1 bis 5, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t dass die Verriegelung der beiden Kassetten-Halbteile durch Eintauchen wenigstens eines Stiftes (9, 10) in die Kassette aufgehoben wird, wobei der Stift auf die Schr·agfl·ache (27) des Sperrhaken-Verbindungssteges (24) trifft und den Haken aus einem Sperrzahn (26) hebt.
7. Video-Wendekassette nach Anspruch 6, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass f·ur jeden Sperrhaken ein Stift zur Entriegelung in die Kassette eintaucht. EMI11.1
 REIBUNG Die Erfindung betrifft eine
Video-Wendekassette in Form eines im wesentlichen quaderf·ormigen
K·orpers mit zwei darin drehbar gelagerten Wickelspulen f·ur das
Magnetband und einer an einer schmalen L·angsfl·ache vorgesehenen
·Offnung mit teilweise zur·uckgesetzter Geh·ausewand zur freiliegenden
Magnetbandf·uhrung, wobei die Kassette vorzugsweise aus zwei
verriegelbaren im wesentlichen geschlossenen Halbteilen besteht, die zur
Ver·anderung des Wickelspulenabstandes sowie zur Vergr·osserung der
freiliegenden Magnetbandl·ange verschiebbar gelagert sind.
REIBUNG Die Erfindung betrifft eine
Video-Wendekassette in Form eines im wesentlichen quaderf·ormigen
K·orpers mit zwei darin drehbar gelagerten Wickelspulen f·ur das
Magnetband und einer an einer schmalen L·angsfl·ache vorgesehenen
·Offnung mit teilweise zur·uckgesetzter Geh·ausewand zur freiliegenden
Magnetbandf·uhrung, wobei die Kassette vorzugsweise aus zwei
verriegelbaren im wesentlichen geschlossenen Halbteilen besteht, die zur
Ver·anderung des Wickelspulenabstandes sowie zur Vergr·osserung der
freiliegenden Magnetbandl·ange verschiebbar gelagert sind.Es sind Magnetbandkassetten bekannt, bei denen die Bandwickelspulen mit einem bestimmten Abstand nebeneinander in einem Kassettengeh·ause angeordnet und die Wickelspulen von aussen ·uber ger·ateseitig angeordnete Antriebsmittel antreibbar sind. Weiterhin sind auch Kassetten bekannt, die eine Ver·anderung des Abstandes der Band wickelspulen erm·oglichen. Derartige Kassetten finden insbesondere bei Videoger·aten Anwendung. Bei Ger·aten dieser Art werden von Seiten des Benutzers, je nach Verwendungszweck, differenzierte Anforderungen gestellt.
So wird z. B. zwischen netzabh·angigen Heimger·aten und netzunabh·angigen, also batteriebetriebenen, tragbaren Ger·aten unterschieden. Hierbei spielt insbesondere das Gewicht und die Gr·osse der unterschiedlichen Ger·ate eine erhebliche Rolle. So ist die Gr·osse des Ger·ates in erheblicher Weise von der Gr·osse der Kassette abh·angig.
Bei einem tragbaren Videoger·at, das beispielsweise die Bildaufzeichnung mit Hilfe einer Videokamera erm·oglichen soll, ist eine lange Aufnahmedauer, wie sie bei einem Heimger·at gew·unscht ist, nicht erforderlich. Dagegen spielen jedoch das Gewicht und die Gr·osse bei einem tragbaren Videoger·at eine erhebliche Rolle.
Aus den unterschiedlichen Anforderungen eines Benutzers an ein Video-Heimger·at einerseits und ein tragbares batteriebetriebenes Videoger·at andererseits ergeben sich zwangsl·aufig abweichende Kassettengr·ossen mit unterschiedlicher Spieldauer. Der naheliegende Wunsch, dass die kleinere, f·ur tragbare Videoger·ate geeignete Kassette, auch auf einem f·ur gr·ossere Kassetten eingerichtetem Heimger·at abgespielt werden soll, ist schwerlich zu realisieren.
Es ist zwar bereits eine Kassettenkonstruktion bekanntgeworden, bei der auch kleinere Kassetten in einem Video-Heimger·at f·ur gr·ossere standardisierte Kassetten abgespielt werden k·onnen, die daf·ur erforderliche Konstruktion ist jedoch recht kompliziert und damit teuer.
So werden gem·ass diesem Stand der Technik Zahnrad·ubersetzungen erforderlich, mit deren Hilfe der Bandwickelabstand ausgeglichen wird.
Ein weiteres Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel zur Anpassung einer kleineren Kassette in ein Heimger·at, das nur f·ur eine gr·ossere Kassette geeignet ist, sieht vor, dass die Wickel spulen in einer besonderen Lagereinrichtung schwenkbar gelagert sind. So k·onnen die Wickel spulen mit einem kleineren Abstand in ein kleineres Kassettengeh·ause und nach Verschwenken in ein gr·osseres Kassettengeh·ause eingesetzt werden. Eine Ausf·uhrung dieser Art ist ebenfalls aufwendig und erfordert vom Benutzer ein besonderes technisches Geschick.
Eine diese Nachteile teilweise vermeidbares Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel einer Kassette zur Ver·anderung des Wickelspulenabstandes sieht vor, die Wickel spulen in getrennten, zueinander verschiebbaren Geh·ausehalbteilen unterzubringen. Die beiden Geh·ausehalbteile werden hierbei durch einen als Hohlzylinder ausgebildeten F·uhrungsabschnitt in einer festen Bewegungsbahn gef·uhrt.
Nachteilig ist hierbei, dass die F·uhrung der beiden Geh·ausehalbteile keinerlei Anpassung der auseinander gezogenen Kassetten-Geh·ausehalbteile an die Lage des im Heimger·at ver·anderten Wickelspulenantriebs erm·oglicht.
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine relativ kleine Video-Wendekassette f·ur tragbare Videoger·at zu schaffen, die mit geringem technischen Aufwand auch in einem f·ur gr·ossere standardisierte Kassetten vorgesehenem Video-Heimger·at abgespielt werden kann, wobei sich der Wickelspulenabstand in der Kassette dem Spulenantrieb im Heimger·at zwangsl·aufig anpasst.
Die L·osung dieser Aufgabe erfolgt erfindungsgem·ass durch die im kennzeichnenden Teil des Anspruchs 1 angegebenen Massnahmen.
Vorteilhafte Weiterbildungen ergeben sich aus den Unteranspr·uchen.
Die Erfindung wird nachfolgend unter Bezugnahme auf die Zeichnungsfiguren beispielsweise erl·autert. Es zeigt: Fig. 1 eine perspektivisch dargestellte Video-Wendekassette mit abgenom mener Abdeckung und verriegelten Kassetten-Halbteilen, Fig. 2 eine perspektivisch dargestellte Video-Wendekassette nach Fig. 1 mit auseinandergezogenen Kasset ten-H
albteilen, Fig. 3 eine schematische Draufsicht auf eine Video-Wendekassette mit aus einandergezogenen Kassetten-Halb teilen nach Fig.2, wobei ein Be reich der Kassetten-Halbteile mit aufgebrochener Geh·ausewand ge zeichnet ist und Fig. 4 eine vergr·osserte Darstellung eines des f·ur die Verriegelung der Kas setten-Halbteile vorgesehenen Sperr hakens.
Die Figur 1 zeigt eine perspektivisch dargestellte Video Wendekassette 1 - kurz Kassette genannt - mit einer von der Kassette abgehommenen Abdeckung 2. Die Abdeckung ist f·ur den normalen Verwendungsfall der Kassette in einem tragbaren Videoger·at stets auf der Kassette aufgesetzt und sch·utzt das sonst freiliegende Magnetband 3. Beim Einlegen der Kassette in ein tragbares Videoger·at wird die Abdeckung automatisch seitlich abgeklappt, und das Magnetband ist f·ur den Zugriff von ger·ateseitig vorhandenen Ausziehstiften (nicht gezeichnet) freiliegend. Die Kassette 1 weist die Form eines im wesentlichen quaderf·ormigen K·orpers auf mit zwei darin drehbar gelagerten Magnetband-Wickelspulen 4, 5. An einer schmalen L·angsfl·ache der Kassette ist eine ·Offnung mit teilweise zur·uckgesetzter Geh·ausewand 6 zur freiliegenden Nagnetband- f·uhrung vorgesehen.
Die Kassette selbst besteht aus zwei im wesentlichen geschlossenen Halbteilen 7, 8. Die einzelnen Kassetten-Halbteile 7, 8 bestehen wiederum aus zwei fast vollst·andig geschlossenen Halbschalen, die zusammengeschraubt oder nach einer der sonst bekannten Verbindungsformen haltbar zusammengef·ugt sind. Beide Kassettenhalbteile 7, 8 sind verriegelbar und k·onnen durch Eindringen von zwei Stiften 9, 10 (strichpunktiert gezeichnet) in an der Kassette vorgesehenen F·uhrungsbohrungen 11, 12 gel·ost werden. Die Kassettenhalbteile sind sodann auf einen vorgesehenen Abstand auseinanderzuziehen.
In der Figur 2 ist die Kassette im auseinandergezogenen Zustand gezeichnet. Die Verbindung der beiden verschiebbaren Kassetten-Halbteile 7, 8 erfolgt ·uber zwei flache F·uhrungsteile 13, 14. Die F·uhrungsteile sind parallel und in geringem Abstand zu den ·ausseren schmalen L·angsfl·achen 15, 16 der Kassetten-Halbteile angeordnet. Die Verriegelung der Kassettenhalbteile erfolgt im geschlossenen Zustand der Kassette ·uber die den F·uhrungsseiten zugeordneten Sperrhaken 17, 18. Die beiden F·uhrungsbohrungen 11, 12 zur Entriegelung der Sperrhaken 17, 18 liegen im Teilungsbereich der beiden Kassetten-Halbteile 7, 8 und bestehen somit aus den vier Bohrungsh·alften 11', 11" und 12', 12''.
Aus der Figur 3 sind weitere Einzelheiten ·uber die Ausgestaltung der Sperrhaken und der Lagerung der F·uhrungsteile 13, 14 in den Kassetten-Halbteilen 7, 8 zu erkennen. Die F·uhrungsteile 13, 14 sind in F·uhrungsnuten 19, 20, die sich im Inneren der Kassetten-Halbteile befinden, gelagert. Um sicherzustellen, dass sich die Kassetten Halbteile 7, 8 nicht nur in Haupterstreckungsrichtung (s. waagerechte Pfeilangabe) der Kassette 1 gegeneinander verschieben lassen, sondern auch in begrenzter Weise senkrecht hierzu (s. senkrechte Pfeilangabe) ausweichen k·onnen, sind die F·uhrungsteile 13, 14 aus schmalem Federbandstahl gefertigt.
Die Bandwickelspulen 4, 5 in der ausgezogenen Kassette k·onnen sich somit der Lage der im Heimger·at befindlichen und gegen·uber dem tragbaren Videoger·at unterschiedlichen Antriebselementen voll anpassen. Zur Begrenzung der Auszugsl·ange der Kassette weisen die F·uhrungsteile 13, 14 Begrenzungsnasen 21 auf.
Die Figur 4 zeigt einen vergr·ossert gezeichneten Ausschnitt des Sperrhakens aus einem Kassetten-Halbteil.
Der Sperrhaken 18 besteht aus einem Hakenteil 22, einem Lagerauge 23 und einem Verbindungssteg 24. Eine Druckfeder 25, die auf dem Verbindungssteg des Sperrhakens aufgesetzt ist und sich im Geh·ause des Kassetten-Halbteils abst·utzt, sorgt f·ur den n·otigen Verriegelungsdruck bei zusammengeschobenen Kassetten-Halbteilen. Im verriegelten Zustand beider Halbteile 7, 8 liegt das Sperr haken-Hakenteil 22 des einen Halbteils in einertrSperr- zahn 26 des anderen Halbteils. ·Uber eine Schr·agfl·ache 27, die sich am Sperrhaken-Verbindungssteg befindet, kann ·uber das Auftreffen eines in die Kassette eintauchenden Stiftes 9, 10 die Verriegelung des Sperrhakens aufgehoben werden. Das Hakenteil 22 des Sperrhakens weist in bekannter Weise eine Anlaufschr·age auf ·Uber einen Lagerstift ist der Sperrhaken 18 im Kassetten-Halbteil drehbar gelagert.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Arrangement for the recording and reproduction of wide frequency band video signal:
Method of recording and reproduction of wide frequency band video signals onto or from a magnetizable recording carrier, carried out by the following means: means for separating
 of the video frequency signals
into first and second signals of lower and upper frequency range
respectively, for converting said second signal into a third signal the
frequency range of which equaling that of said first signal, for
frequency modulating a carrier wave frequency by said first and third
signals and for recording the frequency modulated signals by means of a
twin head, for reproducing the recorded signals by means of a twin head
and for amplifying, limiting and demodulating the recorded signals and
reconverting the third signal into its original frequency range and
combining the so reconverted third signal and said first signal.
of the video frequency signals
into first and second signals of lower and upper frequency range
respectively, for converting said second signal into a third signal the
frequency range of which equaling that of said first signal, for
frequency modulating a carrier wave frequency by said first and third
signals and for recording the frequency modulated signals by means of a
twin head, for reproducing the recorded signals by means of a twin head
and for amplifying, limiting and demodulating the recorded signals and
reconverting the third signal into its original frequency range and
combining the so reconverted third signal and said first signal.1. An apparatus for the recording and reproducing of wide frequency band color video signals onto or from two adjacent tracks of a magnetizable recording carrier, whereat the color video signal to be recorded is separated into a lower and upper frequency range, said lower frequency range frequency modulating a carrier wave, said apparatus further comprising:
a. means for converting said upper frequency range into said lower frequency range;
b. means for frequency modulating said carrier wave by said converted upper frequency range;
c. twin head means for simultaneously recording both said frequency modulated signals; and,
 d. means for reproducing the recorded signals encoding the twin head,
means for amplifying, limiting and demodulating the recorded signals and
for reconverting the converted upper frequency range into its original
frequency range and for combining the reconverted signal and the lower
frequency range signal.
d. means for reproducing the recorded signals encoding the twin head,
means for amplifying, limiting and demodulating the recorded signals and
for reconverting the converted upper frequency range into its original
frequency range and for combining the reconverted signal and the lower
frequency range signal.2. The apparatus in accordance wit
 h claim 1 wherein the
mixing frequency used for the converting and reconverting of the upper
frequency range is an integral multiple of the line frequency.
h claim 1 wherein the
mixing frequency used for the converting and reconverting of the upper
frequency range is an integral multiple of the line frequency.
3. The apparatus in accordance with claim 1 wherein the individual recording heads of the twin head have azimuth-angles which are different from zero and are equal in value but oppositely inclined.
 In view of the
limited band width of the frequency band of simple tape video recording
and reproducing apparatuses for home use a color television signal can
be recorded only with losses in quality and after a considerable
transformation of the original video signals.
In view of the
limited band width of the frequency band of simple tape video recording
and reproducing apparatuses for home use a color television signal can
be recorded only with losses in quality and after a considerable
transformation of the original video signals. For example, in a widely used European system of recording and reproduction, the brightness and chrominance signals are separated from each other. A carrier frequency located at about 4 MHz is frequency-modulated with the brightness signal, which is limited to 2.7 MHz. The chrominance signal is moved out of its original frequency position into a new frequency range, which is located lower than that of the lower side bands of the frequency-modulated brightness signals. Thereafter the frequency-converted color signals are added and recorded.
Japanese systems, which also were developed especiall
 y for home use, use
essentially the same principle. Both systems suffer from serious
disadvantages. The procedure is intricate and includes many
possibilities for error, if the luminance and chrominance signals are
separated, processed in a different manner and then put together again.
The frequency band width of the brightness signal must be narrowed.
Since a portion of the tape recorded information is contained in the
amplitude, the advantage of frequency modulation largely is lost. The
track width cannot be reduced below a certain minimum figure and the
color information is recorded at a relatively large wave length. The
danger of cross-talk and especially cross-color disturbances between
neighboring tracks exists just where it is most conspicuous. This can be
avoided by the provision of guard bands between the tracks, but because
the guard bands do not carry any information a large amount of tape is
needed.
y for home use, use
essentially the same principle. Both systems suffer from serious
disadvantages. The procedure is intricate and includes many
possibilities for error, if the luminance and chrominance signals are
separated, processed in a different manner and then put together again.
The frequency band width of the brightness signal must be narrowed.
Since a portion of the tape recorded information is contained in the
amplitude, the advantage of frequency modulation largely is lost. The
track width cannot be reduced below a certain minimum figure and the
color information is recorded at a relatively large wave length. The
danger of cross-talk and especially cross-color disturbances between
neighboring tracks exists just where it is most conspicuous. This can be
avoided by the provision of guard bands between the tracks, but because
the guard bands do not carry any information a large amount of tape is
needed. If guard bands between adjacent tracks are omitted, adjacent tracks are recorded and read at different azimuth angles, and the polarity of the color information is changed from line to line, which requires not only additional electronics but requires a radically different lay-out of the whole electronic circuit, depending upon whether the apparatus is to be used for NTSC, PAL or SECAM.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
 It
is an object of the present invention to provide a recording and
reproducing arrangement for wide frequency band video signals onto or
from a magnetizable carrier, which avoids the above described faults and
which especially permits the recording of the full video frequency band
with small and inexpensive apparatuses and without additional tape
consumption at full utilization of the advantages of frequency
modulation. The color television system (NTSC, PAL or SECAM) does not
influence the recording, so that the same apparatus can be used for all
systems, except of course, for different power supply frequencies.
It
is an object of the present invention to provide a recording and
reproducing arrangement for wide frequency band video signals onto or
from a magnetizable carrier, which avoids the above described faults and
which especially permits the recording of the full video frequency band
with small and inexpensive apparatuses and without additional tape
consumption at full utilization of the advantages of frequency
modulation. The color television system (NTSC, PAL or SECAM) does not
influence the recording, so that the same apparatus can be used for all
systems, except of course, for different power supply frequencies. The inventive combination is new and brings out a surprising result. For example, the frequency transformation of a portion of the color television signal is known. U.S. Pat. No. 3,234,323 discloses the method of modulation onto a carrier frequency for the brightness and the color and to record each in parallel tracks. German Pat. No. 1,935,109 discloses means to record on adjacent tracks without leaving space in between, but with different azimuth angles. In comparison, none of the known arrangements permits recording of the full color television signal frequenc
 y band with small and inexpensive apparatus independently of
the color transmission system and with full utilization of the
advantages of frequency modulation and without additional tape
consumption and loss of quality.
y band with small and inexpensive apparatus independently of
the color transmission system and with full utilization of the
advantages of frequency modulation and without additional tape
consumption and loss of quality. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIGS. 1 and 2 taken together provide a diagrammatic showing of the subject invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
An embodiment of the in
vention is shown in the FIGS. in which for example the mean track spacing amounts to 187 μm, the width of a track itself is 130 μm, the frequency modulation deviation ranges from 3.1 MHz to 4.5 MHz, and at this condition video signals up to 2.7 MHz with 10 dB loss can be recorded. If now, according to the invention, the mean track spacing is divided into two tracks each of 93.5 μm track width lying parallel and adjacent to one another without interspace, and if, from the signal which is introduced at connection 1, a lower frequency range extending up to 2.7 MHz is separated by a low-pass filter 2, then this lower frequency range may be frequency modulated in a modulator 3 and after appropriate amplification in an amplifier 4 be recorded by a magnetic transducer head 5, just as well as in the aforementioned original state. Simultaneously, the line synchron impulses are separated at 6 and an upper frequency range of the color television signal from 2.7 MHz to 5.5 MHz is made available over the high-pass filter 7. The frequency of the output voltage of a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) 8 with a nominal frequency of about 2.6 MHz is divided in a divider 9 by, for example, 166 and compared with the line synchron impulses in a phase comparator 10; the difference signal synchronizes the oscillator 8 to a frequency which is an integral multiple of the line frequency. The mixing of the output voltages of the
 oscillator 8 and of the high-pass
filter 7 in a mixing unit 11 and the limiting by a low-pass filter 12,
whose cut-off frequency may lie a little higher than those of 2, effects
a transposition of the upper video frequencies into the same frequency
range as is behind the low-pass filter 2; the signals applied to the
frequency modulators 3 and 13, may also be treated in the same manner,
especially with respect to a possible pre-emphasis and the modulation
itself; the last is indicated by a common carrier wave oscillator 16.
The signal, which is frequency modulated in 13, is applied by way of an
amplifier 14 to a further magnetic head 15, which is preferably combined
with the magnetic head 5 to form a twin head, recording simultaneously
with head 5 parallel tracks without any interspace. Technologically, the
amplifiers 4 and 14 and the heads 5 and 15 are of equal design; as
later will be explained, only the azimuth angles of the gaps of heads 5
and 15 differ from each other.
oscillator 8 and of the high-pass
filter 7 in a mixing unit 11 and the limiting by a low-pass filter 12,
whose cut-off frequency may lie a little higher than those of 2, effects
a transposition of the upper video frequencies into the same frequency
range as is behind the low-pass filter 2; the signals applied to the
frequency modulators 3 and 13, may also be treated in the same manner,
especially with respect to a possible pre-emphasis and the modulation
itself; the last is indicated by a common carrier wave oscillator 16.
The signal, which is frequency modulated in 13, is applied by way of an
amplifier 14 to a further magnetic head 15, which is preferably combined
with the magnetic head 5 to form a twin head, recording simultaneously
with head 5 parallel tracks without any interspace. Technologically, the
amplifiers 4 and 14 and the heads 5 and 15 are of equal design; as
later will be explained, only the azimuth angles of the gaps of heads 5
and 15 differ from each other. In the play-back apparatus according to
FIG. 2, the amplifiers 17, the limiters 18 and the demodulators 19, which are following the heads 5 and 15, are once more built wholly alike; the blocks 6, 8, 9, 10 and 11 are the same for recording, according to FIG. 1 and for reproducing, according to FIG. 2. The output voltage of the mixing unit 11 is taken through a band-pass filter 20, which filters out the upper side band of the mixing product, and transfers it to an adder stage 21, which also receives the demodulated signals read by head 5. If necessary, there may be inserted frequency-response corrections at suitable places, deemphasis on offset compensators, and this in both channels.
The synchronization to the line frequency of the mixing frequency of the oscillator 8, which is required for the frequency shift, proves to be especially advantageous, because by this, large time basis deviations are compensated for. The upper cut-off frequency of the demodulated signal, which head 5 picks up, is thus shifted exactly as much as the lower cut-off frequency behind the band-pass filter 2
 0, so that the crossover positions between
the two ranges of video frequencies are not changed relative to each
other.
0, so that the crossover positions between
the two ranges of video frequencies are not changed relative to each
other. As a result, compared with the original shape, the upper useful video frequency can be doubled without loss of playing time or quality, and this, without having to extract the chrominance signal out of the color television signal and without having information carried by the amplitude of the magnetization, which exists at the tape. For this latter reason, the width of the tracks may be further decreased, and in this way, the playing time can be again increased.
Compared with the aforementioned Japanese system, it is true that this system also uses the advantage of abutting tracks. But instead of this, another advantage is obtained in that the very complicated and from television system to television system very different processing of the color signal is avoided; also the disadvantage of a chrominance sub-carrier transposed into a low frequency range, namely the therewith associated danger of cross-talk from track to track is very greatly reduced. For example: the converted chrominance sub-carrier frequency is normally of the order of 600 kHz. If there is a track width without interspace of 55 μm, a head to tape speed of 6000 mm/s and an azimuth-angle of 8° Which is contrarotating from track to track (which means 16° effective for each head), and the scanning head deviates by 9% of the track width out of its track, the cross-talk results in a signal to noise ratio o
 f 20.4
dB. This ratio is too small and must therefore be further diminished by
complicated and expensive electronic means with the help of comb
filters. According to the invention all recorded frequencies are located
at 4 MHz; under otherwise equal circumstances the cross-talk ratio now
amounts to 45 dB, which requires no additional distortion suppressing
means.
f 20.4
dB. This ratio is too small and must therefore be further diminished by
complicated and expensive electronic means with the help of comb
filters. According to the invention all recorded frequencies are located
at 4 MHz; under otherwise equal circumstances the cross-talk ratio now
amounts to 45 dB, which requires no additional distortion suppressing
means. The invention is not limited to the specific oblique track recording, but can also be used at the transverse track, or the longitudinal track methods using rotating magnetic heads. The advantages derived from the invention is independent of the shape (form) of the record carrier and of the track.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Method and device for tracking video signals on a magnetic VIDEO2000 SYSTEM tape by detecting phase jumps:
A method and device for maintaining an exact track when playing back video ignals, which are recorded on a magnetic tape in oblique parallel tracks with different azimuth angles.
1. A device for adjusting the exact position of the track when replaying video signals which are recorded in oblique parallel tracks on a magnetic tape, said oblique tracks being al
 ternately recorded and replayed by two rotating
heads, the gaps of which have opposite equal azimuth angles causing
phase jumps of the line frequency of the scanned video signal during
track changes in case of mistracking, said device including means for
detecting said phase jumps, and means for applying said phase jumps to
said rotating heads to readjust the rotating video heads to the exact
track position by control of the tape speed.
ternately recorded and replayed by two rotating
heads, the gaps of which have opposite equal azimuth angles causing
phase jumps of the line frequency of the scanned video signal during
track changes in case of mistracking, said device including means for
detecting said phase jumps, and means for applying said phase jumps to
said rotating heads to readjust the rotating video heads to the exact
track position by control of the tape speed. 2. A device in accordance with claim 1 further comprising means for measuring the phase jumps of the line frequency for changes from an even numbered to an odd numbered track and for changes from an odd numbered to an even numbered track.
3. A device in accordance with claim 2 in which the phase jumps of the line frequency of the video signal with respect to a reference frequency during subsequent track changes are detected by different sample and hold circuits, the outputs of said sample and hold circuits being fed to the input of a differential amplifier to form an error signal, said error signal controlling the tape speed so as to minimize said error signal.
4. A device according to claim 2 further comprising a phase locked loop to produce the reference frequency synchronized to the line frequency of the scanned video signal, said phase locked loop containing a phase comparator, a voltage controlled oscillator and a low pass filter therebetween, said low pass filter causing the control time constant of the voltage controlled oscillator to equal at least the scanning time of one track.
5. A device according to claim 3 in which the separated line pulses from the scanned video signal are fed through gate circuits to the sample and hold circuits, and which are alternately opened for about two line intervals by pulses which are derived from the position signals of the head wheel each time a video head starts to scan a new track.
6. A device according to claim 5 in which the error signal of the differential amplifier is added to or subtracted from the rectified voltage of the tacho generator of the tape feed motor and in which by comparing the sum or difference, respectively, with a given reference voltage the rotation of the tape feed motor is controlled so as to minimize the error voltage produced by the differential amplifier.
7. A device according to claim 6 in which a low pass filter is provided at the output of the differential amplifier.
When recording video signals in o
 blique parallel tracks cross-talking from track to track
can be kept to a minimum if the tracks are separated by guard bands.
However, such guard bands are a poor way of using the available
recording face.
blique parallel tracks cross-talking from track to track
can be kept to a minimum if the tracks are separated by guard bands.
However, such guard bands are a poor way of using the available
recording face. Another possibility for minimizing cross-talk is to record with azimuth angles which differ from track to track. In such a case the guard bands can be eliminated. However, in such a system the requirement for exactly scanning the recorded track is increased.
Methods and devices for an automatical tracking during play-back of video signals in oblique tracks are known, but were never attractive for incorporation into devices for home use. For example it has been suggested to use the time difference which occurs simultaneously with a migration as a measure of the lateral migration of the replay head from the magnetic track. This method can be accomplished by very simple circuitry but poses high demands with respect to the precision and the timely constancy of such circuits, because very small and continuously changing time intervals must be measured.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The subject invention provides a device and a method wherein an exact tracking is made
 possible without expensive equipment and without
significant requirements for precision, durability and constancy of the
circuit elements.
possible without expensive equipment and without
significant requirements for precision, durability and constancy of the
circuit elements. The invention is related to video tape recorders where the video signals are recorded in oblique parallel tracks which are alternately recorded and replayed by two rotating video heads with gaps having opposite azimuth angles. The migration of the video heads from the exact track position is determined by the phase jump which occurs during track change.
The invention is based on the realization that the sudden change of a magnitude is easier to measure than a continuous change.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
FIG. 1 is a diagrammatic representation of two oblique tracks with the tape scanning and tape feeding directions indicated;
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram utilizing the subject invention; and
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating a further embodiment of the invention.
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
FIG. 1 sho
ws two oblique tracks 1 and 2. For track 1 the recording and replay gap of the magnet head is turned from the vertical position counterclockwise through angle α and for track 2 in a clockwise direction through an equal angle α . If during replay the heads are displaced from the nominal position 3, 4 into position 3', 4' by an amount h perpendicular to the track direction, an additional phase change occurs in addition to the reduction of the signal to noise ratio. With the scanning and tape feeding directions and with the azimuth angles of FIG. 1 head 3' scans the video signal by an amount (h) (tan α) earlier and head 4' by an amount (h) (tan α) later than at nominal position. Therefore, during the change from track 1 to track 2 a sudden phase jump takes place corresponding to (2) (h) (tan α) rearwardly and from track 2 to track 1 forwardly. However, if heads 3 and 4 are not migrating upwardly as shown in FIG. 1 but rather downwardly, the sudden phase jump takes place with the magnitude (2) (h) (tan α) forwardly and from track 2 to track 1 rearwardly. Therefore, the magnitude of the phase jump is a measure of the magnitude of migration of the video heads from the track, while the sign of the phase jump determines the direction of migration.
In the invention the phase jump is measured at the line frequency with respect to a reference oscillation which is synchronized to the line frequency but which cannot follow sudden phase jumps or rapid frequency changes. For this purpose a voltage controlled oscillator 8 is provided as can be seen in FIG. 2 which oscillates at about double the line frequency and which is synchroniz
 ed by means of phase comparator 6 and low pass filter 7 to the
line pulses fed at 5 and separated from the scanned video signal. The
double line frequency is chosen because of the frequency of the
equalizing pulses of the vertical signal, and the low pass filter 7
prevents oscillator 8 from following immediately the occuring phase
jumps.
ed by means of phase comparator 6 and low pass filter 7 to the
line pulses fed at 5 and separated from the scanned video signal. The
double line frequency is chosen because of the frequency of the
equalizing pulses of the vertical signal, and the low pass filter 7
prevents oscillator 8 from following immediately the occuring phase
jumps. Simultaneously, the scanned line pulses are fed to gate circuits 12 and 13 which open for a short time for about two line durations after each second head change. The necessary opening pulses are fed at 14 and 15 and are derived from the position pulse of the head wheel, so that gate 12 opens when changing from track 1 to track 2, for example, while gate 13 opens when changing from track 2 to the next track.
It is useful to transform the output voltage of oscillator 8 into a trapezoidal wave by pulse former 9 the output of which is fed as a reference to the sample and hold circuits 10 and 16 or 11, 16, respectively. The output signals of 10 and 11 are coupled to the input of differential amplifier 17.
The error signal which is generated at t
 he output of the differential amplifier 17 may be used for making
an exact track adjustment for the video heads. For example, the error
signal may influence the recovery time of a monostable multivibrator 18
to which the reference pulses for the servo control circuit 20 of the
tape transport motor are fed at 19. Another possibility exists in the
immediate adjustment of the rotating video heads in axial direction by
means of piezoceramic elements which are excited by the error signal of
differential amplifier 17.
he output of the differential amplifier 17 may be used for making
an exact track adjustment for the video heads. For example, the error
signal may influence the recovery time of a monostable multivibrator 18
to which the reference pulses for the servo control circuit 20 of the
tape transport motor are fed at 19. Another possibility exists in the
immediate adjustment of the rotating video heads in axial direction by
means of piezoceramic elements which are excited by the error signal of
differential amplifier 17. Since the maintaining of the track and the transport speed for the tape are unmistakeably correlated in accordance with the invention the reference pulses which are fed at 19 may be omitted in accordance with a further embodiment of the invention. In other words, the usual synchronous track is not necessary.
In accordance with FIG. 3, the servo control circuit of band feeding motor 21 includes tacho generator 22 which is coupled with motor 21, and the output voltage of the generator after being rectified at 23 is coupled to the input of a differential amplifier 24. The other input of differential amplifier 24 is coupled to a reference voltage 25. This control loop controls the tape feeding speed approximately to the nominal value, while the output voltage of the differential amplifier 17 which is fed into the summing element 26 provides the exact adjustment of the tape speed with respect to the exact track adjustment.
The additional low pass filter 27, 28 is only necessary for the start of the tape movement and elimates the big alternating phase jumps generated during the acceleration of the magnetic tape.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Method for dynamic track adjustment in SYSTEM VIDEO2000 video recorders:.
1. Method for dynamic equidistant track adjustment in magnetic helical-scan video recording with the aid of rotating magnetic video heads which are adjustable by a servosystem perpendicularly to the direction of movement, the servosystem being controlled by a control signal (burst) of a particular frequency keyed in each case at the beginning of the track and the area of reproduction of a new track being located immediately adjacent to the area of recording of the preceding track, characterized in that the order of recording and reproduction for the control signal (burst) keyed in arbitrary length, relative to the scanning movement of the magnetic video head, takes place alternatingly from track to track and, relative to the beginning of the track, offset in time and geometry from track to track.
1. Verfahren zur dynamischen ·aquidistanten Spureinstellung bei der magnetischen Schr·agspur-Videoaufzeichnung mit Hilfe von rotierenden Video-Magnetk·opfen, die senkrecht zur Bewegungsrichtung durch ein Servosystem verstellbar sind, wobei die Ansteuerung des
 Servosystems durch ein jeweils am Spuranfang
eingetastetes Steuersignal (Burst) bestimmter Frequenz erfolgt, d a d u r
c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t dass die Reihenfolge der Aufzeichnung
und Wiedergabe f·ur das in beliebiger L·ange eingetastete Steuersignal
(Burst) bezogen auf die Abtastbewegung des Video Magnetkopfes von Spur
zu Spur alternierend und bezogen auf den Spuranfang von Spur zu Spur
zeitlich und geometrisch versetzt erfolgt, derart, dass der
Wiedergabebereich einer neuen Spur dem Aufzeichnungsbereich der
vorangegangenen Spur unmittelbar benachbart ist.
Servosystems durch ein jeweils am Spuranfang
eingetastetes Steuersignal (Burst) bestimmter Frequenz erfolgt, d a d u r
c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t dass die Reihenfolge der Aufzeichnung
und Wiedergabe f·ur das in beliebiger L·ange eingetastete Steuersignal
(Burst) bezogen auf die Abtastbewegung des Video Magnetkopfes von Spur
zu Spur alternierend und bezogen auf den Spuranfang von Spur zu Spur
zeitlich und geometrisch versetzt erfolgt, derart, dass der
Wiedergabebereich einer neuen Spur dem Aufzeichnungsbereich der
vorangegangenen Spur unmittelbar benachbart ist. 2. Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass in jeder zweiten Spur zwischen dem Aufzeichnungs- und Wiedergabebereich des Steuersignals (Burst) eine L·ucke mit der L·ange des doppelten Spurversatzes eingef·ugt ist.
3. Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass in jeder zweiten Spur die Summe der zeitlichen und geometrischen L·ange des Aufzeichnungs- und Wiedergabebereichs f·ur das Steuersignal (Burst) um den doppelten Spurversatz vergr·ossert wird.
Die Anwendung des Verfahrens setzt voraus, dass die aufzeichnenden bzw. wiedergebenden rotierenden Video Magnetk·opfe senkrecht zu ihrer Abtastrichtung gesteuert bewegbar sind. Die gesteuerte Bewegbarkeit, wie sie z.B. beim System ~Video 2000" angewendet wird, dient prim·ar der Spurfindung bei der Wiedergabe. Hierzu werden zus·atzlich zum Luminanz- und Chrominanzsignal beispielsweise vier Hilfsfrequenzen aufgezeichnet, die unterhalb des Chrominanzsignals und Luminanzsignals liegen und die bei der Wiedergabe in einer Servoschaltung derart verarbeitet werden, dass der Wiedergabekopf immer so eingestellt wird, dass er auf der gewunschten Magnetspur l·auft.
Einzelheiten ·uber dieses Verfahren sind beispielsweise aus WGrundig Technische lnforma- ton
 en", Heft 3/198Q,
Seite 111 ff. und "Grundig Technische Infonmationen", Heft 3/1981, Seite
105 ff. zu entnehmen.
en", Heft 3/198Q,
Seite 111 ff. und "Grundig Technische Infonmationen", Heft 3/1981, Seite
105 ff. zu entnehmen.Die M·oglichkeit der Steuerung der Magnetk·opfe senkrecht zur Spurrichtung wird ausser zur Spurfindung bei der Wiedergabe aber auch bei der Aufnahme dazu benutzt, um die aufeinanderfolgenden Spuren ·aquidistant zu schreiben.
Hierzu wird ein Schwingungszug, auch Burst genannt, am jeweiligen Spuranfang mit einer weiteren Hilfsfrequenz aufgezeichnet. Unmittelbar nach der Aufzeichnung des Burstsignals, dessen Dauer nach dem Stand der Technik dem von Spur zu Spur entstehenden Spurversatz entspricht, wird der rotierende Magnetkopf auf Wiedergabe umgeschaltet und tastet das Burstsignal der vorhergehenden Spur ab. Die Amplitude des da
 bei
gewonnenen Signals ist ein Mass f·ur den Spurabstand und kann zur
Einstellung des rotierenden Magnetkopfes am Spuranfang benutzt werden,
derart, dass die Spurabst·ande konstant sind.
bei
gewonnenen Signals ist ein Mass f·ur den Spurabstand und kann zur
Einstellung des rotierenden Magnetkopfes am Spuranfang benutzt werden,
derart, dass die Spurabst·ande konstant sind.Die Bezugsgr·osse bei diesem Regelvorgang wird beim Stand der Technik dadurch gewonnen, dass einer der beiden rotierenden Video-Magnetk·opfe auf dem Kopf rad hinsichtlich seiner Einstellung senkrecht zur Abtasteinrichtung eine feste Vorgabe erh·alt und nur der zweite Kopf so geregelt wird, dass ·aquidistante Spuren entstehen. Es ist prinzipiell aber auch m·oglich, jeweils bei Beginn einer Aufzeichnung die erste Spur mit fest eingestelltem rotierenden Video-Magnetkopf zu schreiben und anschliessend beide Video-Magnetk·opfe fortlaufend auf konstanten Spurabstand einzuregeln.
F·ur die exakte Spureinstellung darf dabei das Burstsignal nicht zu kurz sein, da mit der nachfolgenden Auswerteschaltung und auch mit der Umschaltung Aufnahme/ Wiedergabe Einschwingvorg·ange mit bestimmter Zeitdauer verbunden sind.
Wird die Aufzeichnung des Burstsignals nach de
m Stand der Technik entsprechend der Dauer des Spurversatzes gew·ahlt, dann liegen die Aufzeichnungsabschnitte in benachbarten Spuren geometrisch treppenf·ormig zueinander wie aus Figur 1 ersichtlich. Der rotierende Magnetkopf kann dann sofort nach der Aufzeichnungsperiode f·ur den Burst auf Wiedergabe umgeschaltet und nach Massgabe des aus der vorhergehenden Spur abgetasteten Burstsignals auf exakten Spurabstand eingestellt werden.
Bei geringer Spurbreite bzw. Bandgeschwindigkeit und entsprechend geringer Spurneigung kann der Spurversatz auf sehr kleine Werte absinken. Entsprechend den oben geschilderten Zusammenh·angen wird dann nach dem Stand der Technik die Dauer des Burstsignals ebenfalls auf einen geringen Wert reduziert. Es besteht dann die Gefahr, dass dieses zeitlich verk·urzte Burstsignal mit R·ucksicht auf die mit der Kopfregelung verbundenen Einschwing- und Urnschaltvorg·ange f·ur eine st·orsichere Regelung nicht mehr ausreicht.
Man k·onnte daran denken, das Burstsignal zeitlich ·uber den Spur versatz hinaus zu verl·angern, um wieder eine sichere Auswertung zu erreichen. Dann aber wandert die geometrische und zeitliche Position des Burstsignals von Spur zu Spur immer weiter auf der Aufzeichnungsspur voran und w·urde schliesslich den Videosignal-Austastbereich verlassen bzw. in den Bildsignalbereich gelangen. Dies ist zur Vermeidung von St·orungen unzul·assig.
Ausserdem l·asst sich bei zunehmender Entfernung der Burstaufzeichnung vom Spuranfang das gew·unschte Ziel der Spureinstellung im Sinne eines konstanten Spurabstandes am Spuranfang nicht mehr befriedigend erreichen.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, bei der magnetischen Video aufzeichnung in Schr·agspuren auch bei geringem Versatz von Spur zu Spur ein Burstsignal f·ur die Einstellung des Spurabstandes aufzuzeichnen und wiederzugeben, das in seiner zeitlichen Ausdehnung so gew·ahl
 t werden kann, dass eine sichere
Auswertung mit Hilfe der Regeleinrichtung f·ur die Verstellung des
Magnetkopfes senkrecht zur Abtastrichtung im Sinne der Erreichung
·aquidistanter Spuren m·oglich ist.
t werden kann, dass eine sichere
Auswertung mit Hilfe der Regeleinrichtung f·ur die Verstellung des
Magnetkopfes senkrecht zur Abtastrichtung im Sinne der Erreichung
·aquidistanter Spuren m·oglich ist.Die erfindungsgem·asse L·osung dieser Aufgabe ist aus Figur 2 ersichtlich. Wird n·amlich die zeitliche Folge der Aufzeichnung und Wiedergabe des Burstsignals von Spur zu Spur alternierend gew·ahlt, dann kann das Burstsignal zeitlich ausgedehnt werden, ohne dass die unerw·unschte Erscheinung der Wanderung innerhalb der Spur in Abtastrichtung auftritt. Im dargestellten Beispiel nach Figur 2 ist in der ersten Spur die geometrische und zeitliche L·ange der Burstaufzeichnung beliebig gew·ahlt. In der folgenden Spur wird nun die Burstaufzeichnung bezogen auf den Spuranfang um die Burstl·ange zuz·uglich des Spurversatzes verschoben und der Lesevorgang vor den Schreibvorgang gelegt. Damit wird der zeitlich verl·angerte Burst vollst·andig ausgewertet und ein neuer Burst mit der gleichen L·ange aufgezeichnet.
In der dritten Spur schliesslich setzt die Burstaufzeichnung bezogen auf den Spuranfang wieder so ein wie in der ersten Spur, w·ahrend der Lesevorgang gegen·uber der Aufzeichnung um die Burstl·ange zuz·uglich des doppelten Spurversatzes verschoben ist. Durch Vertauschung der Reihenfolge von Schreiben und Lesen sowie durch Einf·ugen einer L·ucke zwischen Schreiben und Lesen in jeder zweiten Spur um die Dauer des doppelten Spurversatzes wird also sichergestellt, dass bei verl·angerter Burstdauer das Burstsignal in voller L·ange gelesen werden kann und trotzdem der Schreib- und Lesevorgang am Spuranfang verbleibt, wie es f·ur die wirkungsvolle und st·orsichere Regelung des Spurabstandes n·otig ist.
Ausserdem wird durch die erfindungsgem·asse Auf zeichnungs- Wiedergabe-Geometrie f·ur das Steuersignal (Burst) erreicht, dass jedem der beiden Magnetk·opfe ein konstanter zeitlicher Ablauf f·ur Aufzeichnung und Wie
 dergabe zugeordnet
ist. Mit anderen Worten, der erste Videokopf (ungeradzahlige Spuren)
zeichnet in festem Abstand oder zeitlicher Dauer vom Spuranfang auf,
dann folgt eine L·ucke entsprechend dem doppelten Spurversatz, danach
der Wiedergabebereich f·ur das Steuersignal (Burst).
dergabe zugeordnet
ist. Mit anderen Worten, der erste Videokopf (ungeradzahlige Spuren)
zeichnet in festem Abstand oder zeitlicher Dauer vom Spuranfang auf,
dann folgt eine L·ucke entsprechend dem doppelten Spurversatz, danach
der Wiedergabebereich f·ur das Steuersignal (Burst).Der zweite Videokopf (geradzahlige Spuren) gibt in festem Abstand oder zeitlicher Dauer vom Spuranfang wieder und zeichnet ohne l·ucke anschliessend auf.
Zum besseren Verst·andnis des Verfahrens sei noch angemerkt, dass die Wiedergabe des Steuersignals (Burst) aus der vorhergehenden Spur trotz Winkelentkopplung auch dann noch m·oglich ist, wenn der Video-Magnetkopf die vorhergehende Spur nicht mehr unmittelbar trifft.
Dies erkl·art sich daraus, dass die Frequenz des Steuersignals bezogen auf das Video signal verh·altnism·assig niedrig gew·ahlt wird, so dass die Winkelentkopplung unwirksam wird und das Streufeld ·uber die Spurbreite hinaus wirkt.
DEVICE FOR ROTATING ANNULAR TRANSFORMERS IN A VIDEO SET:
1. Arrangement of rotating toroidal transformers (10, 11) for the inductive transmission of high-frequency oscillations in a video recording and playback machine with at least two signal recording and playback heads (5, 6), which are preferably arranged offset by 180 degrees on a rotating head wheel (2) in a head drum, the transformers each having one rotating (10', 11') toroidal part and one fixed (10", 11") toroidal part, each signal head (5, 6) being assigned the rotating part of a transformer in a certain way, and the transformers (10, 11) being arranged axially one above the other, characterized in that the transformers (10, 11) have different ring sizes such that they do not radially overlap.
1. Anordnung von rotierenden ringf·ormigen Transformatoren zur induktiven ·Ubertragung hochfrequente
r Schwingungen in einem Video-Auf zeichnungs- und -Wiedergabeger·at mit wenigstens zwei Signal-Aufzeichnungs- und Wiedergabek·opfen, die vorzugsweise um 180 versetzt auf einem rotierenden Kopfrad in einer Kopftrommel angeordnet sind, und jedem Signalkopf der rotierende Teil eines Transformators in bestimmter Weise zugeordnet ist, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass ein Transformator (10) mit rotierendem und feststehendem ringf·ormigem Teil des ersten Signalkopfes (5) gegen·uber dem anderen rotierenden Transformator (11) des zweiten Signalkopf es (6) axial verschoben und durch verschiedene Ringgr·ossen radial und axial nicht ·uber schneidend in der Kopftrommel (1) angeordnet ist.
2. Anordnung nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass das Kopfrad (2) einen hochgezogenen Flansch (13) aufweist, auf den ein rotierender Trafoteil (11) aufgesetzt ist, w·ahrend der andere rotierende Trafoteil mit der geringeren Ringgr·osse (10') auf der inneren Planseite des Kopfrades (14) angeordnet ist, und die H·ohe des Flansches wenigstens der gesamten Querschnittsh·ohe eines Transformators entspricht.
3. Anordnung nach Anspruch 2, d a d u r c g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass die H·ohe des Flansches des Kopfrades der halben Querschnittsh·ohe des kompletten Transformators entspricht.
Bei den meisten bekannten magnetischen Bild-Aufzeichnungs- und Wiedergabeger·aten mit bandf·ormigem Aufzeichnungsmedium erfolgt die Aufzeichnung und Wiedergabe der Video signale auf das Magnetband mittels sogenannter Schr·agspuraufzeichnung bzw. Abtastung ·uber auf einem rotierenden Kopfrad angeordnete Videok·opfe.
Es ist bekannt, dass hierbei die hochfrequenten Schwingungen mit Hilfe eines rotierenden Transformators induktiv ·ubertragen werden. Da vorzugsweise mit zwei um 1800 auf dem Kopfrad versetzt angeordneten Videok·opfen gearbeitet wird, sind auch hierzu zwei getrennte rotierende Transformatoren erforderlich. Das Kopfrad mit den beiden Videok·opfen ist mit den rotierenden Transformatoren in einer vom Magnetband teilweise umschlungenen zweigeteilten Kopftrommel integriert, wobei wenigstens ein Teil der Kopftrommel feststeht. Die Unterbringung der beiden rotierenden Transformatoren erfolgt in bekannter Weise in der Kopftrommel derart, dass diese entweder axial ·ubereinander angeordnet sind, oder sich mit verschiedenen Radien der einzelnen ·Ubertragerringe in einer Ebene befinden.
Ein wesentlicher Unterschied dieser verschiedenen Anordnungen ergibt sich in der Bewertung der Ubersprechd·ampfung von einem zum anderen rotierenden Transformator. Eine messwertm·assig grosse Obersprechd·ampfung ist bei Ger·aten der geschilderten Art in zunehmender Weise w·unschenswert, da inzwischen auch das Stereo-Tonsignal im Schr·agspurverfahren aufgezeichnet bzw. abgetastet wird.
Es kann somit in Videoaufzeichnungsger·aten ein PCM Tonsignal in einer Zusatzumschlingung vor oder nach der Video spur aufgezeichnet werden. Besonders hohe Anforderungen an die ·Ubersprechd·ampfung zwischen den beiden rotierenden Signal·ubertragern (Transformatoren) werden dann noch gestellt, wenn bei dieser genannten Technik eine Nachvertonung gew·unscht wird, denn dann ist es erforderlich, dass ein Videokopf mit dem PCM Schreibstrom angesteuert wird, w·ahrend der andere Videokopf das frequenzmodulierte Videosignal ausliest Die hierf·ur erforderliche hohe Ubersprechd·ampfung ist nach den bisher bekannten Anordnungen von rotierenden Transformatoren in der Kopftrommel eines Videoaufzeichnungsger·ates nicht gegeben.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es daher, eine Anordnung und Ausf·uhrung von wenigstens zwei rotierenden Transformatoren in Videoaufzeichnungsger·aten zu schaffen, die einerseits ein gutes ·Ubersprechverhalten sicherstellt und andererseits einen einfachen konstruktiven Einb
 au der rotierenden
Transformatoren in die Kopftrommel des Ger·ates gew·ahrleistet.
au der rotierenden
Transformatoren in die Kopftrommel des Ger·ates gew·ahrleistet.Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgem·ass durch die im kennzeichnenden Teil des Anspruchs 1 angegebenen Merkmale gel·ost.
Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen des erfindungsgem·assen Aufbaus eines rotierenden ringf·ormigen Transformators in einer Kopftrommel f·ur Videoaufzeichnungsger·ate ergeben sich aus den Unteranspr·uchen.
Ein Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel wird nachfolgend anhand einer schematischen Zeichnung n·aher erl·autert.
Die im Schnitt dargestellte Figur zeigt eine Kopftrommel 1 mit eingesetztem Kopfrad 2. Der obere Teil 3 der Kopftrommel ist mit dem Kopfrad drehbar in einem unteren Teil 4 der Kopftrommel gelagert. Auf beiden Seiten um 180 versetzt, sind die Signalk·opfe 5 und 6 auf dem Kopfrad angeordnet. Auf einer nur teilweise dargestellten Welle 7 ist das Kopfrad aufgezogen und ·uber zwei Kugellager 8 in der Kopftrommel gelagert. Zur Vereinfachung der dargestellten Figur ist der Antrieb der Kopftrommel nicht gezeichnet, ebenso ist der Chassisteil 9, auf dem die Kopftrommel befestigt ist, nur zeichnungsm·assig angedeutet. Die beiden rotierenden Transformatoren 10 und 11 sind versetzt in der Kopftrommel angeordnet, wobei der Transformator 10 dem Signalkopf 5 und der Transformator 11 dem Signalkopf 6 zugeordnet ist.
Die Anschl·usse der Signalk·opfe werden jeweils ·uber eine Kontaktplatte 12, die sich im oberen Teil der Kopftrommel befindet, zu den Transformatoren 10 und 11 gef·uhrt. Die rotierenden Transformatoren bestehen, wie bekannt, aus zwei Ringkernh·alften mit eingelegten Wicklungen, wobei der jeweils rotierende Teil 10' und 11' an dem Kopfrad und der feststehende Teil 10'' und 11'' am unteren Teil der Kopftrommel befestigt ist. Die beiden Ringteile sind durch einen sehr kleinen Luftspalt getrennt. Die Anschl·usse der feststehenden Trafo-Ringteile werden in einfachster Weise ·uber Bohrungen, die sich im unteren Teil der Kopftrommel befinden, an eine nicht n·aher dargestellte Schaltungsplatte gef·uhrt.
Nach der Zeichnung ist der Transformator 10, der dem ersten Signalkopf 5 zugeordnet ist, gegen·uber dem anderen Transformator 11, der dem zweiten Signalkopf 6 zugeordnet ist, axial verschoben und durch verschiedene Ringgr·osse radial und axial nicht ·uberschneidend in der Kopftrommel angeordnet. Um diese Anordnung zu erreichen, weist das Kopfrad 2 einen ·ausseren hochgezogenen Flansch 13 auf, an dem der rotierende Trafoteil 11' des Trafos 11 (mit grossem Ringdurchmesser) befestigt ist. Der rotierende Trafoteil 1
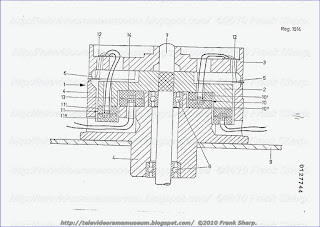 0' mit der geringeren Ringgr·osse befindet sich
hingegen auf der inneren Planseite 14 des Kopfrades. Die H·ohe des
Flansches entspricht bei dieser Anordnung wenigstens der gesamten
Querschnittsh·ohe eines kompletten Transformators.
0' mit der geringeren Ringgr·osse befindet sich
hingegen auf der inneren Planseite 14 des Kopfrades. Die H·ohe des
Flansches entspricht bei dieser Anordnung wenigstens der gesamten
Querschnittsh·ohe eines kompletten Transformators.Eine andere nicht dargestellte Anordnung sieht eine Flanschh·ohe vor, die etwa nur der halben Querschnittsh·ohe des Transformators entspricht.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 System for extending the playing time of video cassettes in VIDEO2000 SYSTEM.
A system is provided for extending the playing time of standardized video cassettes. The system utilizes a rotating head drum having mounted thereon a first set of video heads displaced 180° with respect to each other, a second set of video heads displaced by a certain amount from 180° with respect to each other, a rotating winding of a transformer, and relays to interconnect the heads of either the first or second set of heads with the rotating winding as the head drum rotates. The relays are controlled by stationary coils and logic to respond to the setting of switches to enable the system to operate at normal tape speed via the first set of heads or reduced tape speed via the second set of heads without requiring any change in the speed of rotation of the head drum.
1. In a video tape record/playback machine of the type including a tape transport, a tape transport drive, a rotating head drum, means for rotating said head drum, a first pair of video heads mounted on said head drum and displaced from each ot
 her by 180°, and a
transformer having a rotating winding mounted to said head drum and a
stationary winding; the improvement comprising: a second pair of video
heads mounted to said head drum and displaced from each other by an
angle slightly different from 180° and control means to interconnect
said first pair of video heads and said rotating winding when said tape
transport drive is operated at a normal speed and to interconnect at
least one of the video heads of said second pair and said rotating
winding when said tape transport drive is operated at a lower, extended
play speed.
her by 180°, and a
transformer having a rotating winding mounted to said head drum and a
stationary winding; the improvement comprising: a second pair of video
heads mounted to said head drum and displaced from each other by an
angle slightly different from 180° and control means to interconnect
said first pair of video heads and said rotating winding when said tape
transport drive is operated at a normal speed and to interconnect at
least one of the video heads of said second pair and said rotating
winding when said tape transport drive is operated at a lower, extended
play speed. 2. The machine in accordance with claim 1 wherein said control means comprises: a first polarized relay affixed to said head drum for rotation therewith, said first relay having a first position interconnecting said first pair of video heads to said rotating winding and a second position interconnecting said second pair of video heads to said rotating winding;
first and second stationary exciter coils in controlling relationship with said first relay to drive said first relay to said first or second position;
switch means having a "normal" position and a "long play" position; and
logic circuit means responsive to the "normal" or "long play" position of said switch means to activate said exciter coils to drive said first relay to said first or second position respectively.
3. The machine in accordance with claim 2 wherein said second pair of video heads comprises a record/playback head and a playback only head; said switch means further has a "record" position and a "playback" position and further comprising
a second polarized relay affixed to said head drum for rotation therewith and having a "playback" position interconnecting both heads of said second pair of video heads with said rotating winding and a "record" position interconnecting only said record/playback head with said rotating winding;
said first and second stationary exciter coils are in controlling relationship with said second relay to drive said second relay to said "record" or "playback" position; and
said logic circuit means is responsive to said "record" or "playback" position of said switch to activate said exciter coils to drive said second relay to said "record" or "playback" position respectively.
4. The machine in accordance wit
 h claim 3 wherein said
switch means further includes a "start" position indicating that said
tape transport drive has been activated and said logic circuit means is
responsive to said "start" position of said switch to activate said
exciter coils to drive said first relay to said first position
regardless of whether said switch is in said "normal" or "long play"
position.
h claim 3 wherein said
switch means further includes a "start" position indicating that said
tape transport drive has been activated and said logic circuit means is
responsive to said "start" position of said switch to activate said
exciter coils to drive said first relay to said first position
regardless of whether said switch is in said "normal" or "long play"
position. 5. The machine in accordance with claim 1 further comprising a servo control connected to said tape transport drive, a tachometer generator secured to said tape transport drive adapted to generate pulses responsive to the rotational speed of said drive; a tape transported past said head drum by said tape transport, said tape having thereon first and second slant tracks, and the nominal output of said tachometer generator at said normal and lower speeds are integral multiples of the frame frequency of said slant tracks.
6. The machine in accordance with claim 5 further comprising: a divider connected to the output of said tachometer generator, said divider having a first state to divide the output of said tachometer generator by a first fixed integer to reduce it to the frame frequency when said tape transport operates at normal speed and a second state to divide the output of said tachometer generator by a second fixed integer to reduce it to the frame frequency when said tape transport operates at a lower speed;
a comparator having a first input from said divider, a second input from a reference pulse source, and an output in controlling relationship with said servo control;
a reference pulse source; and
means for switching said reference pulse source between a first state to generate reference pulses corresponding to said normal speed and a second state to generate reference pulses corresponding to said lower speed.
7. Video tape cassette recorder provided for the use of standardized V2000 video cassettes and for
 extending the playing time of said
video cassettes, said recorder including a tape transport mechanism
capable of driving the tape at a normal standardized speed and at
essentially half the standardized speed, a rotating head drum with a
first pair of video heads displaced from each other by 180° and with a
second pair of video heads displayed from each other by an angle
slightly different from 180° and displaced from said first pair by a
suitable angle; a transformer with one stationary winding and one
rotating winding mounted to said head drum, said head drum being
equipped with a first polarized relay to connect said first or said
second pair of video heads to said rotating transformer winding and with
a second polarized relay to connect one or both of said second pair of
video heads to said rotating transformer winding; said first and said
second polarized relays being displaced from each other by 180° and
being actuated in both positions by first and second stationary coils
excited through logic circuits under the control of position pulses of
said head drum and of the switching mode of operative switches, said
operative switches being shiftable between normal or long play or record
or playback positions.
extending the playing time of said
video cassettes, said recorder including a tape transport mechanism
capable of driving the tape at a normal standardized speed and at
essentially half the standardized speed, a rotating head drum with a
first pair of video heads displaced from each other by 180° and with a
second pair of video heads displayed from each other by an angle
slightly different from 180° and displaced from said first pair by a
suitable angle; a transformer with one stationary winding and one
rotating winding mounted to said head drum, said head drum being
equipped with a first polarized relay to connect said first or said
second pair of video heads to said rotating transformer winding and with
a second polarized relay to connect one or both of said second pair of
video heads to said rotating transformer winding; said first and said
second polarized relays being displaced from each other by 180° and
being actuated in both positions by first and second stationary coils
excited through logic circuits under the control of position pulses of
said head drum and of the switching mode of operative switches, said
operative switches being shiftable between normal or long play or record
or playback positions. 8. A video tape cassette recorder in accordance with claim 7 wherein said operative switches include a special switch for the start and the stop of the tape transport drive; said special switch being interconnected with said logic circuits so as to connect in the stop position of said special switch said first pair of video heads to said rotating transformer winding regardless of whether said respective operative switch is in the normal or in the long play mode position.
9. A video tape cassette recorder in accordance with claim 7 further comprising a tachometer generator and a frequency divider for the output pulses of said tachometer generator; said tachometer generator being secured to and producing a plurality of pulses per revolution of said tape transport drive; the frequency of said tachometer generator output pulses being an integral multiple of the frame frequency of the video signal at both the rated normal and the rated low speed of said tape transport drive; and said frequency divider being switchable between two division factors so as to divide to frame frequency the frequency of said tachometer generator output pulses at both, the rated normal and the rated low speed of said tape transport drive.
The present invention relates to video tape recording and mor
 e particularly to a
system for extending the playing time of standardized video cassettes in
which each of two rotating video heads, displaced relative to each
other by 180°, records or scans one slant track per television field.
e particularly to a
system for extending the playing time of standardized video cassettes in
which each of two rotating video heads, displaced relative to each
other by 180°, records or scans one slant track per television field. In the standard video cassette intended for home use, a magnetic tape located in a cassette is utilized. When the cassette is positioned in the video equipment, the tape is pulled from the cassette and positioned for operation. In order to permit interchangeability of the cassette (i.e., in order to insure that a cassette recorded on one machine can be played back on another machine) certain system standards have been established which are adhered to by the industry. These standards include the geometry of the slant tracks, the speed of rotation of the head drum, the number of video heads mounted on the drum, and the transport speed of the tape past the head drum. In one popular cassette system two video heads are mounted on the head drum 180° apart from each other and displaced to record or scan along one slant track. With 50 fields per second (as is common in most European countries) the head drum must therefore rotate at 1500 RPM. In order that the common line interlace of 312.5 lines per field is recorded and reproduced correctly, a tape speed must be chosen so that the spacing between the tracks (in the lengthwise direction of the tape) corresponds to an odd multiple of half lines. In the aforementioned system, this multiple was chosen as 11.
As a result of the above established standards, the maximum playing time of a cassette is limited to about an hour utilizing the thinnest tapes available. This playing time is not sufficient for certain forms of desired programs (e.g., such as full-length motion pictures). Thus, a considerable need exists for a system to extend the playing time of a standard cassette while maintaining provision for normal recording and playback capabilities.
It has heretofore been propose
 d (in German Pat. No. 1,437,141 for example) that the
playing time of a given length of tape could be extended through the
slant track method by recording only the even or odd television fields
but scanning them twice during playback with the tape transport moving
at roughly half the normal speed. In practice, a head drum which rotates
at 1500 RPM and carries two video heads is utilized. The magnetic tape
is looped 180° over the head drum. For recording, only one of the heads
operates while for playing back both heads scan the same track. It is
also known that in this case the two heads must no longer be precisely
180° apart from each other but the additional head position must be
displaced by a slight amount from 180°. In practice this displacement
distance is on the order of a millimeter and thus, it would not be
practical to mount an additional head displaced by this slight amount.
d (in German Pat. No. 1,437,141 for example) that the
playing time of a given length of tape could be extended through the
slant track method by recording only the even or odd television fields
but scanning them twice during playback with the tape transport moving
at roughly half the normal speed. In practice, a head drum which rotates
at 1500 RPM and carries two video heads is utilized. The magnetic tape
is looped 180° over the head drum. For recording, only one of the heads
operates while for playing back both heads scan the same track. It is
also known that in this case the two heads must no longer be precisely
180° apart from each other but the additional head position must be
displaced by a slight amount from 180°. In practice this displacement
distance is on the order of a millimeter and thus, it would not be
practical to mount an additional head displaced by this slight amount. The principal object of the present invention is to provide an improved video cassette machine capable of functioning in both a standard normal mode and an extended play mode.
A further object is to provide such a machine which can be readily switched from one mode to the other without requiring any intervention with the drive mechanism of the head drum.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
 The above and
other beneficial objects and advantages are attained in accordance with
the present invention by providing an improved video tape
record/playback machine capable of normal as well as extended play
operation. Video tape record/playback machine includes a tape transport,
a tape transport drive, a rotating head drum, a motor for rotating the
head drum, a first pair of video heads mounted on the head drum and
displaced from each other by 180° of arc, and a transformer having a
rotating winding mounted to the head drum and a stationary winding. In
addition to the above, the present device further includes a second pair
of video heads mounted to the head drum and displaced by an angle
slightly different from 180°. In addition, means are provided to
interconnect the first pair of video heads and the rotating winding when
the tape transport drive is operated at a normal speed and to
interconnect at least one of the video heads of the second set and the
rotating winding of the transformer when the tape transport drive is
operated at a lower, extended play speed. The control means includes a
set of polarized relays affixed to the head drum for rotation therewith
as well as stationary exciter coils which activate the relays. The
exciter coils, in turn, are activated through a control logic circuit
which is governed by switches set at the desired operational mode.
The above and
other beneficial objects and advantages are attained in accordance with
the present invention by providing an improved video tape
record/playback machine capable of normal as well as extended play
operation. Video tape record/playback machine includes a tape transport,
a tape transport drive, a rotating head drum, a motor for rotating the
head drum, a first pair of video heads mounted on the head drum and
displaced from each other by 180° of arc, and a transformer having a
rotating winding mounted to the head drum and a stationary winding. In
addition to the above, the present device further includes a second pair
of video heads mounted to the head drum and displaced by an angle
slightly different from 180°. In addition, means are provided to
interconnect the first pair of video heads and the rotating winding when
the tape transport drive is operated at a normal speed and to
interconnect at least one of the video heads of the second set and the
rotating winding of the transformer when the tape transport drive is
operated at a lower, extended play speed. The control means includes a
set of polarized relays affixed to the head drum for rotation therewith
as well as stationary exciter coils which activate the relays. The
exciter coils, in turn, are activated through a control logic circuit
which is governed by switches set at the desired operational mode.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the accompanying drawings:
FIG. 1 is a schematic of the head drum and its control logic;
FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of the switching arrangement between the normal and long playing heads; and
FIG. 3 is a schematic of the tape speed switching arrangement.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREPARED EMBODIMENT
Reference is now made to the drawings wherein similar components bear the same reference numeral throughout the several views.
In FIG. 1, a rotating drum head 1 is shown carrying a first set of heads N1 and N2 displaced 180° apart from each other f1 could theoretically be used with another head displaced slightly apart from N2 by a distance on the order of 1 millimeter. Since this is not practical to effect, a second set of heads L1 and L2 is mounted to the head drum with the displacement between heads L1 and L2 being off slightly from 180° as shown. The arrows adjacent to the heads N1, N2, L1 and L2 depict their operability. Accordingly, heads N1, N2 and L1 are designed for record and playback operation while head L2 is designed for playback operation only.
or normal (N mode) operation. For long playing (L mode) operation head N
Referring briefly to FIG. 2, it can be seen that a rotating transformer 2 is provided with one rotating winding and one stationary winding. Since rotating multiple transformers are expensive, only a simple transformer 2 is provided. As shown in FIG. 1, a small polarized relay 3 rotates with the head drum and serves to connect the rotating winding of the transformer with heads N1 -N2 or L1 -L2 as required. To this end, the relay 3 is switched by stationary exciter coils 4 and 5 as the head drum rotates. A second polarized relay 6 is also provided to connect both heads L1 and L2 to the transformer winding during L mode-playback b
 ut only head L1 to the transformer winding during L mode-record. The electrical contacts of the polarized relays 3 and 6 are shown in FIG. 2.
ut only head L1 to the transformer winding during L mode-record. The electrical contacts of the polarized relays 3 and 6 are shown in FIG. 2. The logic and switches for the control of the polarized relays 3 and 6 is depicted in FIG. 1. Thus, as shown, coil 4 is energized by the output of AND gates 7 or 8. Coil 5 is energized by the output of AND gates 9 or 10. In turn, each of the AND gates 7, 8, 9 and 10 has an input from the function switches 11 used to determine (a) L or N mode; (b) record or playback; and (c) whether the tape transport is operative or not.
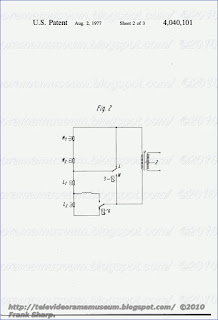 In
addition to the above, gates 7 and 9 each have another input connected
to a position pickup 13. Pickup 13 comprises a simple transducer
designed to generate a pulse each time a small permanent magnet 14 which
rotates with the head drum rotates past the pickup. Thus, the polarized
relay 3 is activated through coils 4 or 5 each time the magnet 14 moves
past the position pickup and is therefore controlled by either the
gates 7 or 9 depending on whether switch 11 is in the "L" or "N"
position.
In
addition to the above, gates 7 and 9 each have another input connected
to a position pickup 13. Pickup 13 comprises a simple transducer
designed to generate a pulse each time a small permanent magnet 14 which
rotates with the head drum rotates past the pickup. Thus, the polarized
relay 3 is activated through coils 4 or 5 each time the magnet 14 moves
past the position pickup and is therefore controlled by either the
gates 7 or 9 depending on whether switch 11 is in the "L" or "N"
position. The output of pickup 13 is also delayed 20 ms through delay means 12 and then applied to gates 8 and 10. 20 ms corresponds to the time it takes for the drum head 1, rotating at 1500 RPM, to rotate through 180°. Thus, 20 ms or half a head drum rotation after relay 3 is excited by coils 4 or 5, relay 6 is excited by coils 4 or 5.
In N mode (i.e., switch 11 at N position) the electrical contacts of relay 3 are switched to N thereby connecting the heads N1 and N2 in series with the rotating transformer. The position of the contacts of relay 6 is immaterial since in N position relay 3 shunts past heads L1 and L2. The operation of the cassette system then proceeds in a conventional manner.
In L mode -- record, (switch 11 at L and "record") the electrical contacts of relay 3 are switched to the L position via the AND gate 15, the OR gate 16 and AND gate 9. After 20 ms, relay 6 is energized via gates 15 and 8 and the head L1 is thereby connected to rotating transformer 2.
In L mode -- playback (switch 11 at L and "playback") one must differentiate between the tape in the running or stopped condition. The latter would occur, for example, for the reproduction of still pictures. It has been found that with the magnetic tape stopped, even when in the "L" mode, the N heads must be utilized since the L heads will incorrectly scan the tracks resulting in phase shift and poor signal to noise ratio. Thus, if switch 11 is in the L mode -- playback position but the tape drive is not started, relay 3 is switched to the N position via inverted AND gate 17, AND gate 18, and AND gate 7.
When the tape drive is started (and switch 11 is thus in the L mode -- playback, tape start position) the relay 3 is switched to the L position via AND gate 19, OR gate 16 and AND gate 9. In addition 20 ms later relay 6 is energized to the playback position via AND gate 10 so that the two heads L1 and L2 are connected in series with the transformer coil 2.
In both the N and L modes of operation the start of ea
 ch slant track has
to coincide with the start of a field and hence phase control of the
head drum 2 is required. This is accomplished by means of a phase
comparator 20 which compares pulses from the pickup 13 with reference
pulses from an outside reference source 21. The reference pulses could,
for example, comprise the vertical synchronous pulses separated from the
video signal. The output of the comparator 21 is fed to an amplifier 22
which feeds the drive motor 23 of the head drum 1.
ch slant track has
to coincide with the start of a field and hence phase control of the
head drum 2 is required. This is accomplished by means of a phase
comparator 20 which compares pulses from the pickup 13 with reference
pulses from an outside reference source 21. The reference pulses could,
for example, comprise the vertical synchronous pulses separated from the
video signal. The output of the comparator 21 is fed to an amplifier 22
which feeds the drive motor 23 of the head drum 1. A phase shifter 24 is provided between the comparator 20 and pickup 13 to compensate for tolerances of the apparatus. The phase difference corresponding to the angle α in FIG. 1 which occurs in the transition from N to L operation is compensated for via switch 25.
Usually, during recording, the servo control of the tape transport motor compares the frequency and phase of the actual values of a tachometer generator coupled with the transport shaft with reference values which generally are derived from the frame frequency and which are simultaneously recorded on the magnetic tape as a separate synchronization track. Here the control accuracy of the tape transport becomes greater, the larger the number of pulses which are delivered by the tachometer generator per revolution of the transport shaft. The previously mentioned conditions for the mutual spacing of the slant tracks recorded on the tape and the dependence of this spacing on line duration also applies analogously to L-operation. Howe
 ver, since in L-operation only every other field is
recorded the track spacing, as measured in the lengthwise direction of
the tape, must now correspond to an odd multiple of whole lines. The
result is that the transport velocity of the magnetic tape in
L-operation must not be exactly equal to one-half of that in
N-operation, but may be somewhat greater or smaller.
ver, since in L-operation only every other field is
recorded the track spacing, as measured in the lengthwise direction of
the tape, must now correspond to an odd multiple of whole lines. The
result is that the transport velocity of the magnetic tape in
L-operation must not be exactly equal to one-half of that in
N-operation, but may be somewhat greater or smaller. In the present case with a track spacing in N-operation corresponding to 11 half-lines, a track spacing corresponding to five whole lines must therefore be chosen in L-operation, i.e., the speed of rotation of the transport shaft must be reduced in the ratio of 5:11. The frequency of the pulses delivered by the tachometer generator is thereby also decreased in the ratio of 5:11.
In order to carry out the switching of the speed between N- and L- operation as simply as possible and, also, by purely electrical means, the number of tachometer pulses per revolution of the transport shaft is chosen so that the tachometer pulse frequencies which occur at the desired speed of the magnetic tape in N- and L- operation are integral multiples of the frame frequency. If, therefore, Z is the number of tachometer pulses per revolution of the transport shaft, and if nN and nL are its speed of rotation in N- and L-operation, the following is to apply: Z . nN = p . 25 and Z . nL = q . 25,
where p and q are integral numbers and 25 Hz is the frame frequency. Since the ratio of the speeds of rotation is the same as that of the line numbers corresponding to the track spacings, therefore, in the example above nN /nL = 11/5 and p/q = 11/5.
FIG. 3 shows the circuit diagram of the transport shaft control and of the transport speed switching arrangement. For simplicity, only the recording operation is shown. Motor 26 drives the magnetic tape in the direction of the arrow via the transport shaft 27 and a rubber pressure roller (not shown). A tachometer generator is coupled to the transport shaft. This may consist of a ferromagnetic gear 29 and a pickup 30 which generates pulses in response to rotation of the gear. The tachometer pulses are fed via an amplifier 31 to a frequency comparator 32 and a switchable frequency divider 33. The time constant of an R-C circuit or the charging time of a capacitor can serve as the reference for comparator 32. Both of these can be adjusted by simple means via the double-throw switch 34 to the pulse frequencies coming from pickup 30 in N- or L-operation. A divider 33 divides the tachometer pulse frequency down to the frame frequency, where the division ratio can be changed by means of switch 35 from p:1 in N-operation to q:1 in L-operation. The actual frame frequency appearing at the output of divider 33 is phase-compared in comparator 36 with the reference frame frequency and the error signal so produced also serves as an input to control the frequency comparator 32.
The reference frame frequency is obtained in the frequency divider 37 by halving the vertical blanking frequency, which is separated from the video signal to be recorded and is fed to the terminal 38. This frame frequency is recorded at the same time on the tape 28 as the sychronization track 40 via the stationary magnetic head 39. The resulting error signal produced in 32 controls the motor 26 via the control amplifier 41.
With the numbers given above, the number of teeth of the ferromagnetic gear tachometer 29 can, for example, be chosen as 110. If the desired speed of rotation of the motor 26 is 750 RPM in N-operation, p = 55 and q = 25 for the divider 33.
The switches 34 and 35 shown in FIG. 3 can be ganged to operate together with the N/L switch 11. To prevent operating errors, it is advisable, however, to operate the switch 25 via the control logic rather than manually.
Thus in accordance with the above, the aforementioned objectives are effectively attained.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Helical scan apparatus for video tape or the like and having rotating-head inclination-adjustment means:
A helical scan recording and playback apparatus wherein magnetic video tape forms a helix about the peripheral surfaces of two coaxial drums which define an annular gap for magnetic heads which orbit in a chamber between the drums and engage inclined tracks at the inner side of the helix. The heads are mounted on a disk which is rotatable on a sleeve surrounding with clearance a shaft for the drums and having an internal protuberance which is tiltable with respect to the periphery of the shaft by a rod extending through an opening in the flange of one of the drums. The inclination of the plane of orbital movement of the heads relative to the central symmetry plane of the gap is changed when the speed of lengthwise movement of tape during playback deviates from the speed of lengthwise movement of tape during recording.
1. In a helical scan apparatus wherein information is recorded on or reproduced from magnetic tape which is moved lengthwise and forms a helix about the peripheral surfaces to two coax
 ial drums
which surround a shaft, wherein the peripheral surfaces of said drums
define an annular gap for at least one magnetic head which orbits in a
first plane and thereby engages inclined tracks of said helix, and
wherein said gap has a central symmetry plane which is normal to the
common axis of said drums, a combination comprising a carrier for said
head, said carrier being disposed between said drums; means for rotating
said carrier to thereby orbit said head along said gap; and means for
changing the inclination of said first plane relative to said symmetry
plane when the speed of tape movement during reproduction deviates from
the speed of tape movement during recording so as to conform the path of
said head to the inclination of tracks on said helix, comprising a
bearing assembly for said carrier and including a sleeve intermediate
said drums and rotatably supporting said carrier coaxial with the same,
said sleeve having an internal surface spacedly surrounding said shaft
and having a protuberance tiltably engaging the periphery of said shaft,
and tilting means actuatable for tilting said bearing assembly with
respect to the common axis of said drums to thereby change the
inclination of said sleeve.
ial drums
which surround a shaft, wherein the peripheral surfaces of said drums
define an annular gap for at least one magnetic head which orbits in a
first plane and thereby engages inclined tracks of said helix, and
wherein said gap has a central symmetry plane which is normal to the
common axis of said drums, a combination comprising a carrier for said
head, said carrier being disposed between said drums; means for rotating
said carrier to thereby orbit said head along said gap; and means for
changing the inclination of said first plane relative to said symmetry
plane when the speed of tape movement during reproduction deviates from
the speed of tape movement during recording so as to conform the path of
said head to the inclination of tracks on said helix, comprising a
bearing assembly for said carrier and including a sleeve intermediate
said drums and rotatably supporting said carrier coaxial with the same,
said sleeve having an internal surface spacedly surrounding said shaft
and having a protuberance tiltably engaging the periphery of said shaft,
and tilting means actuatable for tilting said bearing assembly with
respect to the common axis of said drums to thereby change the
inclination of said sleeve. 2. A combination as defined in claim 1, wherein said protuberance is an annulus.
3. A combination as defined in claim 1, wherein said protuberance engages said shaft in said symmetry plane.
4. A combination as defined in claim 1, wherein said protuberance is a bearing.
5. A combination as defined in claim 1, further comprising means for yieldably urging said sleeve to a position in which said carrier is coaxial with said drums.
6. A combination as defined in claim 1, wherein one of said drums has an opening and said tilting means comprises a rod rigid with said sleeve and extending through said opening.
7. A combination as defined in claim 1, further comprising antifriction bearing means interposed between said carrier and said sleeve.
8. A combination as defined in claim 1, further comprising an energy source for said head, including a rotor mounted on said carrier and electrically connected with said head and a stator mounted on said bearing assembly adjacent to said rotor.
The present invention relates to apparatus for recording and/or reproducing high-frequency information on magnetic tape, and more particularly to a mechanism for guiding magnetic tape and one or more magnetic heads in such apparatus.
It is already known to guide magnetic tape along the peripheral surfaces to two coaxial drums which define an annular gap for one or more magnetic heads mounted in the interior of the drum and serving to record or reproduce information on the tape. The diameters of the peripheral surfaces are identical or nearly identical and the portion of tape which engages such peripheral surfaces forms a helical loop (e.g., an alpha loop or an omega loop). One of both drums may be driven or head against rotation about their common axis. The magnetic head or heads are mounted on a carrier or bracket which relates about the common axis of and is located between the drums. The plane in which the carrier rotates the head or heads coincides with the central plane of the gap between the peripheral surfaces of the drums.
In recording-reproducing apparatus which employ video tape, the speed at which the tape moves during recording may but need not equal the tape speed during reproduction. Thus, it is often desired to accelerate the reproduction, to make slow-motion reproductions of recorded information or to reproduce still images of a particular subject or scene. This creates problems in the aforedescribed apparatus wherein the tape portions which is trained around the peripheral surfaces of the drums forms a helix. As is known, such guidance of the tape is desirable because it allows for relatively high signal density in each of the scan lines which is particularly desirable in connection with recording of television signals, i.e., an entire image can be recorded on a single relatively long track. The track makes an acute angle with the marginal portions of the tape. The inclination of the track is determined primarily by two factors, namely by inclination of the tape with respect to the common axis of the drums and by speed of lengthwise movement of the tape. If the direction of movement of the tape about the drums is identical with the direction of rotation of the heads, the inclination of the track with respect to the marginal portions of the tape increases with increasing speed of the tape. On the other hand, the inclination of the track decreases if the tape is being advanced counter to the direction of rotation of the heads and the speed of the tape incr
 eases.
eases. If the speed of reproduction in a video system is less than the speed during recording, i.e., if the reproduction is to furnish a slow-motion or still-image effect, portions of the heads leave the adjacent tracks with the result that the quality of a substantial portion of the reproduced image is less than satisfactory, i.e., the reproduction takes place with a much less satisfactory signal to noise ratio.
Certain presently known helical scan apparatus are equipped with complex and expensive electronic systems which are designed to compensate for or suppress the just described phenomena. It is also known to employ a mechanical compensating system which is designed to change the path of tape with respect to the drums, i.e., to change the lead of the helical loop which engages the drums. Such proposal is not satisfactory because the tape undergoes undesirable deformation and also because the change in lead is not reproducible, with a requisite degree of accuracy owing to friction with the drums.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the invention is to provide an apparatus which insures proper registry o
 f magnetic heads with the inclined track on a helically wound
magnetic tape by resorting to a small number of simple, rugged and
inexpensive parts.
f magnetic heads with the inclined track on a helically wound
magnetic tape by resorting to a small number of simple, rugged and
inexpensive parts. Another object of the invention is to provide s single mechanical device which maintains the magnetic heads of a helical scan apparatus in accurate register with the track even if the speed of magnetic tape during reproduction varies and deviates from the speed during recording.
A further object of the invention is to provide a helical scan apparatus with a device which insures accurate register of the magnetic head with inclined tracks on a helically looped magnetic tape during reproduction with slow-motion, still-image and/or acceleration effect.
The invention is embodied in a helical scan apparatus wherein information is recorded on or reproduced from magnetic tape which is moved lengthwise and forms a helix about the peripheral surfaces of two coaxial drums, wherein the peripheral surfaces of the drums define an annular gap for at least one magnetic head which orbits in a first plane and thereby engages inclined tracks at the inner side of the helix, and wherein the gap has a central symmetry plane which is normal to the common axis of the drums. The apparatus comprises a carrier (e.g., a disk) which supports the head or heads and is located between the drums, a belt transmission or analogous means for rotating the carrier to thereby orbit the head or heads along the gap, and means for changing the inclination of the first plane with respect to the symmetry plane of the gap when the speed of tape movement during reproduction (playback) deviates from the speed of tape movement during recording so as to conform the path of orbital movement of the head or heads to the inclination of tracks on the helix.
The inclination changing means preferably comprises a bearing assembly for the carrier and means for tilting the bearing assembly with respect to the common axis
 of the drums.
of the drums. The drums are mounted on a common shaft and the bearing assembly preferably comprises a sleeve which is disposed intermediate the drums and rotatably supports the carrier. The sleeve has an internal surface which spacedly surrounds the shaft and has a preferably annular protuberance (e.g., a spherical or prismatic bearing) which tiltably engages the periphery of the shaft. The tilting means is actuatable to change the inclination of the sleeve which is coaxial with the carrier so that the inclination of the first plane with respect to the symmetry plane changes in response to tilting of the sleeve. The protuberance is preferably located in or immediately adjacent to the symmetry plane. The sleeve is held against axial movement relative to the shaft.
The novel features which are considered as characteristic of the invention are set forth in the appended claims. The improved helical scan apparatus itself, however, both as to its construction and its mode of operation, together with additional features and advantages thereof, will be best understood upon perusal of the following detailed description of certain specific embodiments with reference to the accompanying drawing.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
FIG. 1 is a fragmetary partly diagrammatic axial sectional view of a helical scan apparatus which embodies the invention; and
FIG. 2 is a smaller-scale plan view of the apparatus.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
FIG. 1 shows a portion of the improved helica
l scan apparatus which comprises two coaxial drums 1 and 1' having peripheral surfaces 1A, 1A' of identical or nearly identical diameter and serving to guide a video tape 20 (FIG. 2) which can form a so-called alpha or a so-called omega loop (omega loop shown in FIG. 2). The drums 1 and 1' are mounted on a common shaft 2 and their peripheral surfaces 1A, 1A' are spaced apart to define an annular clearance or gap 3 surrounding the endless path of one or more magnetic heads 4 mounted on a disk-shaped carrier 5 which is tiltably mounted on the shaft 2 in the chamber or space 101 defined by the drums 1 and 1'. As a rule, the carrier 5 supports two heads 4 which are located diametrically opposite each other with respect to the axis of the shaft 2. The hub 5a of the carrier 5 is mounted on two antifriction ball bearings 6, 6' which surround a tiltable bearing sleeve 7 mounted in the chamber 101 and having an internal surface surrounding, with certain clearance, the shaft 2.
The energy source for the head or heads 4 includes a transformer having a rotor 8 mounted on the carrier 5 and a stator 9 mounted in the drum 1'. The means for rotating the carrier 5 includes a drive having a motor 19 (FIG. 2) an endless belt or cord 10 engaging a sheave-like portion of the hub 5a.
The internal surface of the bearing sleeve 7 has an annular bearing portion or protuberance 11 which engages with the peripheral surface of the shaft 2 in or very close to the central symmetry plane X--X of the gap 3. The aforementioned clearance between the internal surface of the bearing sleeve 7 and the peripheral surface of the shaft 2 has a first portion at one side and a second portion at the other side of the bearing portion 11. The upper end of the bearing sleeve 7 (as viewed in the drawing) has a larger-diameter portion or collar 13 which is connected with a pin- or rod-shaped tilting member 12 extending with clearance through an opening ID' in the flange 1B' of the drum 1'. If the member 12 is pushed or pulled in the direction indicated by arrow A or B, or moved axially, the sleeve 7 is tilted with respect to the shaft 2 and thereby changes the inclination of the plane of orbital movement of heads 4 with respect to the symmetry plane X--X of the gap 3. Thus, by moving the member 12, one can move the tape-contacting portion of the head 4 above or below the central plane of the gap 3. This enables the head 4 to conform to the changed position of scan lines on video tape 20 which is being moved along the gap 3, with or relative to the peripheral surface 1A and/or 1A'. The position tracks on the tape with respect to the head 4 changes if the speed of tape, during reproduction of information, deviates from the speed during recording. A package of dished springs 14 is interposed between the flange 1B' and the collar 13 to bear against the collar and to bias the sleeve 7 to a desired neutral position while permitting for tilting of the sleeve in response to shifting of the member 12. The carrier 5 shares the tilting movements of sleeve 7 under the action of the member 12. In FIG. 1, the plane of orbital movement of the heads 4 coincides with the symmetry plane X--X.
FIG. 2 shows that the tape 20 is being paid out by a supply reel 21 and is being collected by a takeup reel 22. The means for moving the tape 20 lengthwise comprises a pinch roller 23, a capstan 24 and a motor 25 which drives the capstan 24. Rollers 26 guide the tape 20 between the reel 21 and the peripheral surfaces 1A, 1A' of the drums 1, 1' (only the drum 1' is shown in FIG. 2) as well as between such peripheral surfaces and the capstan 24. The carrier 5 is driven by the aforementioned motor 19. The means for tilting or otherwise moving the rod 12 relative to the shaft 2 is not shown in FIG. 2.
The tiltable mounting of carrier 5 with bearing assembly 6, 6', 7, 11 can be modified in a number of ways without departing from the spirit of the invention. For example, the antifriction bearings 6, 6' can be replaced with a single bearing located in the plane of the gap 3. Moreover, one can replace the protuberance 11 with a tiltable prismatic or spherical antifriction bearing. All that counts is to ins
 ure that the carrier 5 can be tilted
relative to the gap 3 and preferably rotated relative to the shaft 2
while the helical scan apparatus is in use. It has been found that the
illustrated arrangement performs quite satisfactorily and can stand long
periods of use.
ure that the carrier 5 can be tilted
relative to the gap 3 and preferably rotated relative to the shaft 2
while the helical scan apparatus is in use. It has been found that the
illustrated arrangement performs quite satisfactorily and can stand long
periods of use. Without further analysis, the foregoing will so fully reveal the gist of the present invention that others can, by applying current knowledge, readily adapt it for various applications without omitting features which fairly constitute essential characteristics of the generic and specific aspects of my contribution to the art and, therefore, such adaptations should and are intended to be comprehended within the meaning and range of equivalence of the claims.
What is claimed as new and desired to be protected by Letters Patent is set forth in the appended claims.
MINERVA (GRUNDIG) VIDEO 2000 VIDEO2X8 Device for the track following of rotating magnetic heads SYSTEM VIDEO2000. (DYNAMIC TRACK FOLLOWING)
 characterized in that the free length (b) of the
piezoelectric elements (4, 5) extends up to approximately level with the
point of rotation and in that, to compensate for azimut errors, the
piezoelectric elements (4, 5) are clamped into the rotating holder (1)
at such an angle that the clamping lengths (a1 , a2 ) at the edges of
the respective piezoelectric element are of different sizes.
characterized in that the free length (b) of the
piezoelectric elements (4, 5) extends up to approximately level with the
point of rotation and in that, to compensate for azimut errors, the
piezoelectric elements (4, 5) are clamped into the rotating holder (1)
at such an angle that the clamping lengths (a1 , a2 ) at the edges of
the respective piezoelectric element are of different sizes. 1. Einrichtung f·ur die Spurna
 chf·uhrung von rotierenden
Magnetk·opfen in Magnetbandger·aten, bei der als Tr·ager der
Magnetk·opfe Piezoelemente verwendet sind, die an einem Ende fest in
einer rotierenden Halterung eingespannt und an ihrem auslenkbaren Ende
mit dem Magnetkopf verbunden sind, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n
e t , dass zur Erh·ohung der Auslenkung die freie L·ange (b) der
Piezoelemente (4, 5) schr·ag zur Verbindungslinie (6, 7) zwischen
zugeordnetem Magnetkopf (2, 3) und Drehpunkt (8) der rotierenden
Halterung (1) bis etwa in der H·ohe dieses Drehpunktes verl·auft, und
dass zur Kompensation von Azimutfehlern die Piezoelemente schr·ag (a1,
a2) in die rotierende Halterung eingespannt sind.
chf·uhrung von rotierenden
Magnetk·opfen in Magnetbandger·aten, bei der als Tr·ager der
Magnetk·opfe Piezoelemente verwendet sind, die an einem Ende fest in
einer rotierenden Halterung eingespannt und an ihrem auslenkbaren Ende
mit dem Magnetkopf verbunden sind, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n
e t , dass zur Erh·ohung der Auslenkung die freie L·ange (b) der
Piezoelemente (4, 5) schr·ag zur Verbindungslinie (6, 7) zwischen
zugeordnetem Magnetkopf (2, 3) und Drehpunkt (8) der rotierenden
Halterung (1) bis etwa in der H·ohe dieses Drehpunktes verl·auft, und
dass zur Kompensation von Azimutfehlern die Piezoelemente schr·ag (a1,
a2) in die rotierende Halterung eingespannt sind. 2. Einrichtung nach Anspruch 1, d a d u r c h g e k e n n z e i c h n e t , dass die rotierende Halterung der Piezoelemente fest mit einem rotierenden Kopfrad (1) verbunden ist.
indung betrifft eine Einrichtung f·ur die Spurnachf·uhrung von rotierenden Magnetk·opfen in Magnetbandger·aten, bei der als Tr·ager der Magnetk·opfe Piezoelemente verwendet sind, die an einem Ende fest in einer rotierenden Halterung eingespannt und an ihrem auslenkbaren Ende mit dem Magnetkopf verbunden sind.
Seit einiger Zeit werden beispielsweise in Videorecordern zur Spurnachf·uhrung Piezoelemente (in diesem Zusammenhang auch "Aktuatoren" oder Bimorphe" genannt) verwendet, an deren freischwingenden Enden die Magnetk·opfe befestigt sind. Die Piezoelemente weisen die Eigenschaft auf, dass sie beim Anlegen einer Spannung je nach Polarit·at in die eine oder andere Richtung ausgelenkt werden, so dass die Magnet k·opfe senkrecht zur Abtastrichtung bewegt werden k·onnen. Steuert man die Piezoelemente mit einer Regelspannung entsprechend dem Spurfehler an, so folgen die Videok·opfe genau den vorgesehenen Spuren.
An ihren anderen Enden sind die Piezoelemente fest in einen Piezoeiementhalter eingespannt, der entweder selbst rotiert oder starr mit dem rotierenden Kopfrad des Videorecorders verbunden ist. Die freischwingende L·ange des Piezoelementes ist ein Mass f·ur die erreichbare Kopfauslenkung.
Die Figuren 1 und 2 zeigen bekannte Anordnungen zur Spurnachf·uhrung in Videorecordern. Die Magnetk·opfe 2 und 3 sind an den freischwingenden Enden der Piezoelemente 4 und 5 befestigt (z. B. aufgeklebt). Die freischwingenden L·angen der Piezoelemente sind mit b bezeichnet. An ihren anderen Enden sind die Piezoelemente in einen Piezoelementhalter 1 eingesp
 annt, der
entweder selbst als rotierendes Teil ausgebildet oder mit dem
rotierenden Kopfrad des Videorecorders starr verbunden ist. Die
Einspannl·ange der Piezoelemente in die Piezoelementhalter ist mit a
bezeichnet.
annt, der
entweder selbst als rotierendes Teil ausgebildet oder mit dem
rotierenden Kopfrad des Videorecorders starr verbunden ist. Die
Einspannl·ange der Piezoelemente in die Piezoelementhalter ist mit a
bezeichnet.Neuere Trends in der Video technik f·uhren zu immer kleineren Kopf r·adern, was zur Folge hat, dass die freischwingenden L·angen der Piezoelemente und damit auch die erreichbare Kopfauslenkung immer kleiner wird.
Der vorliegenden Erfindung liegt deshalb die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Einrichtung zur Erh·ohung der Piezoelementauslenkung zu schaffen, die sich insbesondere f·ur kleine Magnetbandger·ate eignet, billig ist und eine praktisch azimutfehlerfreie Wiedergabe der magnetisch aufgezeichneten Signale erm·oglicht.
Diese Aufgabe wird nach der vorliegenden Erfindung dadurch gel·ost, dass die Piezoelemente schr·ag zur Verbindungslinie zwischen zugeordnetem Magnetkopf und Drehpunkt der rotierenden Halterung bis etwa in die H·ohe dieses Drehpunktes verlaufen und dass die Piezoelemente zur Vermeidung von Azimutfehlern schr·ag in die rotierende Halterung eingespannt sind.
Die Vorteile der Erfindung liegen darin, dass insbesondere bei Magnetbandger·aten mit kleinen Kopfr·adern die freischwingenden L·angen der Piezoelemente und damit die erreichbare Auslenkung vergr·ossert wird.
Im folgenden wird ein Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel f·ur die vorliegende Erfindung mit Hilfe der Figur 3 n·aher erl·autert. Die Magnetk·opfe 2 und 3 sind an den freischwingenden Enden der Piezoelemente 4 und 5 befestigt. Die freischwingenden L·angen'der Piezoelemente sind mit b bezeichnet.
 Durch
die Anordnung der Piezoelemente 4, 5 schr·ag zur Verbindungslinie 6, 7
zwischen zugeordnetem Magnetkopf 2, 3 und Drehpunkt 8 der rotierenden
Halterung 1 bis etwa in H·ohe dieses Drehpunktes wird die
freischwingende L·ange jedes Piezoelementes vergr·ossert. An ihren
anderen Enden sind die Piezoelemente in den Piezoelementhalter 1
eingespannt.
Durch
die Anordnung der Piezoelemente 4, 5 schr·ag zur Verbindungslinie 6, 7
zwischen zugeordnetem Magnetkopf 2, 3 und Drehpunkt 8 der rotierenden
Halterung 1 bis etwa in H·ohe dieses Drehpunktes wird die
freischwingende L·ange jedes Piezoelementes vergr·ossert. An ihren
anderen Enden sind die Piezoelemente in den Piezoelementhalter 1
eingespannt.Diese Einspannung erfolgt im Gegensatz zum Stand der Technik schr·ag, um die sonst bei der Auslenkung der Piezoelemente zu erwartenden Azimutfehler der Magnetk·opfe zu kompensieren. Damit wird eine praktisch azimutfehlerfreie Wiedergabe der magnetisch aufgezeichneten Signale erm·oglicht. Die Einspannl·ange, unter der hier der Mittelwert der Strecken al und a2 verstanden wird, ist mit a bezeichnet.
Mit einer Anordnung nach der vorliegenden Erfindung wird erreicht, dass im Vergleich zum Stand der Technik bei sonst gleichen Bedingungen (insbesondere bei gleicher Regelspannung)die erreichbare Auslenkung der Piezoelemente vergr·ossert wird.
Die Erfindung ist nicht auf das vorliegende Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel beschr·ankt. Beispielsweise spielt es keine Rolle, welcher Art die Verbindungen zwischen Magnetkopf und Piezoelement sowie Piezoelement und Piezoelementhalter sind.
 ades eine Bandeingriffphase und
eine Nichteingriffphase hat, und wobei an das Piezoelement eines Kopfes,
der gerade im Bandeingriff steht, eine Spannung angelegt wird, die den
Kopf auf der vorgesehenen Spur h·alt, und wobei an das Piezoelement
eines Kopfes, der gerade nicht im Bandeingriff steht, eine abklingende
Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung von Hystereseeffekten des Piezoelementes
angelegt wird, gekennzeichnet durch die folgenden Merkmale: : - die
abklingende Wechselspannung ist rechteckf·ormig und - die Frequenz der
abklingenden Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung von Hystereseeffekten des
Piezoelemen tes liegt knapp unterhalb der mechanischen Reso nanzfrequenz
des Piezoelementes.
ades eine Bandeingriffphase und
eine Nichteingriffphase hat, und wobei an das Piezoelement eines Kopfes,
der gerade im Bandeingriff steht, eine Spannung angelegt wird, die den
Kopf auf der vorgesehenen Spur h·alt, und wobei an das Piezoelement
eines Kopfes, der gerade nicht im Bandeingriff steht, eine abklingende
Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung von Hystereseeffekten des Piezoelementes
angelegt wird, gekennzeichnet durch die folgenden Merkmale: : - die
abklingende Wechselspannung ist rechteckf·ormig und - die Frequenz der
abklingenden Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung von Hystereseeffekten des
Piezoelemen tes liegt knapp unterhalb der mechanischen Reso nanzfrequenz
des Piezoelementes. recorder
 n mit einem rotierenden
Kopfrad, wobei die Magnetk·opfe an Piezoelementen befestigt sind und
jeder Kopf w·ahrend einer Vollumdrehung des Kopfrades eine
Bandeingriffphase und eine Nichteingriffphase hat, und wobei an das
Piezoelement eines Kopfes, der gerade imBandeingriff steht, eine
Spannung angelegt wird, die den Kopf auf der vorgesehenen Spur h·alt,
und wobei an das Piezoelement eines Kopfes, der gerade nicht im
Bandeingriff steht, eine abklingende Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung des
Hystereseeffektes des Piezoelementes angelegt wird.
n mit einem rotierenden
Kopfrad, wobei die Magnetk·opfe an Piezoelementen befestigt sind und
jeder Kopf w·ahrend einer Vollumdrehung des Kopfrades eine
Bandeingriffphase und eine Nichteingriffphase hat, und wobei an das
Piezoelement eines Kopfes, der gerade imBandeingriff steht, eine
Spannung angelegt wird, die den Kopf auf der vorgesehenen Spur h·alt,
und wobei an das Piezoelement eines Kopfes, der gerade nicht im
Bandeingriff steht, eine abklingende Wechselspannung zur Beseitigung des
Hystereseeffektes des Piezoelementes angelegt wird.Seit einiger Zeit werden in Videorecordern zur exakten Spurhaltung Piezoelemente (in diesem Zusammenhang auch "Aktuatoren" oder Eimorphe" genannt) verwendet, auf denen die Magnetk·opfe befestigt sind. Die Piezoelemente weisen die Eigenschaft auf, dass sie beim Anlegen einer Spannung je nach Polarit·at in die eine oder in- die andere Richtung ausgelenirwerden, so dass die Magnetk·opfe senkrecht zur Abtastrichtung bewegt werden k·onnen. Steuert man die Piezoelemente mit einer Regelspannung entsprechend dem Spurfehler an, so folgen die Videok·opfe genau den vorgesehenen Spuren.
Aus der europ·aischen Offenlegungsschrift mit der Publikationsnummer 0091 750 ist eine Anordnung zur Spursteuerung bekannt, bei der ein auf einem Piezoelement befestigter Magnetkopf w·ahrend der Bandeingriffsphase durch das Anlegen einer positiven oder negativen Gleichspannung an eine vorgegebene Stelle gebracht wird. Nach dem Abschalten dieser Gleichspannung am Beginn der Nichteingriffsphase kehrt die Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit nicht wieder exakt in ihre Ausgangsposition zur·uck, da aufgrund des Hystereseeffektes im Piezoe
 lement eine Restauslenkung verbleibt, die die Nullpunktlage der
Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit ver·andert. Demzufolge werden bei der
n·achsten Bandeingriffsphase dieses Kopfes Spurfehler auftreten.
lement eine Restauslenkung verbleibt, die die Nullpunktlage der
Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit ver·andert. Demzufolge werden bei der
n·achsten Bandeingriffsphase dieses Kopfes Spurfehler auftreten.Um diese m·oglichst schnell auszuregeln, ·uberlagert man der an das Piezoelement angelegten Gleichspannung w·ahrend der Nichteingriffsphase eine abklingende sinusf·ormige Wechselspannung. Nach dem Abklingen dieser sinusf·ormigen Wechselspannung liegt am Piezoelement die Spannung an, die die jeweils geforderte Ablenkung des Magnetkopfes bewirkt.
Des weiteren ist aus der europ·aischen Offenlegungsschrift mit der Publikationsnummer 0091 764 eine Vorrichtung bekannt, die ebenso wie der Erfindungsgegenstand zur Spurregelung den Piezoeffekt ausnutzt.
Bei der bekannten Vorrichtung sind zwei um 180 Grad versetzte Magnetk·opfe an Piezoelementen befestigt, die ihrerseits fest mit dem Kopfrad verbunden sind.
Zur Vermeidung eines Spurfehlers bei im Vergleich zur Aufzeichnung unterschiedlicher Wiedergabegeschwin digkeit wird an die beiden Piezoelemente w·ahrend des jeweilyFn Bandeingriffs ein dreieckf·ormiges Spurkorrektursignal angelegt. W·ahrend des Nicht eingriffs beh·alt das Piezoelement und damit auch der daran befestigte Magnetkopf eine Restauslenkung, so dass auch bei dieser Anordnung die Nullpunktlage der Kopf Piezoelement-Einheit ver·andert wird, was am Beginn der n·achsten Bandeingriffsphase des Magnetkopfes zu einem Spurfehler f·uhrt.
Zur Vermeidung dieses Spurfehlers am Beginn der n·achsten Bandeingriffsphase w
 ird dem Piezoelement w·ahrend der
Nichteingriffsphase eine abklingende sinusf·ormige Wechselspannung
zugef·uhrt, die die fehlerhafte Nullpunktlage der Kopf
Piezoelement-Einheit beseitigt, d. h. die Restauslenkung des Kopfes
r·uckg·angig macht, so dass der Kopf am Beginn der n·achsten
Bandeingriffsphase genau die jewei1ige Soll-Spur ·ubereckt. Die bekannte
Vorrich tung enth·alt weiterhin eine Umpolvorrichtung, die in
Abh·angigkeit davon, ob das Piezoelement in die eine oder in die andere
Richtung ausgelenkt wurde, d. h.
ird dem Piezoelement w·ahrend der
Nichteingriffsphase eine abklingende sinusf·ormige Wechselspannung
zugef·uhrt, die die fehlerhafte Nullpunktlage der Kopf
Piezoelement-Einheit beseitigt, d. h. die Restauslenkung des Kopfes
r·uckg·angig macht, so dass der Kopf am Beginn der n·achsten
Bandeingriffsphase genau die jewei1ige Soll-Spur ·ubereckt. Die bekannte
Vorrich tung enth·alt weiterhin eine Umpolvorrichtung, die in
Abh·angigkeit davon, ob das Piezoelement in die eine oder in die andere
Richtung ausgelenkt wurde, d. h.die Wiedergabegeschwindigkeit kleiner oder gr·osser als die Aufzeichnungsgeschwindigkeit war, dem Piezoelement eine geeignet gepolte Spannung zur Beseitigung von Hystereseefekten zuf·uhrt. Es zeigt sich also, dass der Versuch, die Hystereseefekte ohne Verwendung, einer Umpolvorrichtung f·ur die abkleme Weckselspannung zu beseitigen, noch keine zufried stellenden Ergebnisse bringt.
Ausgehend von diesem Stand der Technik liegt der vorliegenden Erfindung die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine verbesserte Anordnung zur Beseitigung von Hysterese- effekten einer Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit zu schaffen, mit der auch ohne Verwendung einer Umpolvorrichtung die Hystereseefekte der Kopf-Piezoelement- Einheit vollst·andig beseitigt werden.
Die L·osung dieser Aufgabe erfolgt durch die kennzeichneneden Merkmale des Patentanspruchs.
Die Vorteile der Erfindung liegen nicht nur darin, dass die Videnkopfe am beginn ihrer n·achsten Bandeingriffsphase an ihrer Sollposition stehen, sondern in der mehrere auch darin dass eine Desensibilizierung der Piezoelment verwenden wird, also keine Verringerung der Empfindlichkeit gegen·uber der angeleg ten Spannung auftritt, was bei einem l·angeren Anlie gen einer Spannung (insbesondere einer hohen Gleich spannung) an einem Piezoelement der Fall sein k·onnte.
im folgenden wird die Erfindung an einem Ausf·uhrungs beispiel n·aher erl·autert. Dabei zeigen: Fig. 1 ein Blockschaltbild mit allen f·ur die Erfindung wesentlichen Bauteilen und Fig. 2 ein Diagramm, das die Verl·aufe der an die Piezoelemente angelegten Spannun gen als Funktion der Zeit zeigt.
Im Ausf·uhrungsbeispiel von Figur 1 wird dem Eingang A eines Microcomputers 1 eine auf bekannte Art und Weise erzeugte digitale, impulsbreitenvariable Regelspan nung zugef·uhrt, die eine genaue Auskunft ·uber die Ab weichung des jeweiligen Magnetkopfes von der Soll spurlage gibt. Eine detaillierte Beschreibung der Er zeugung einer derartigen Regelspannung kann beispielsweise der Zeit schrift "Grundig Technische Informationen" 3/81, S. 110 - 116, entnommen werden.
Der Microcomputer 1 erzeugt an seinem Ausgang B vom jeweiligen Betriebszustand (Aufzeichnung, Wiedergabe, Zeitlupe, Zeitraffer) abh·angige digitale Regelsignale f·ur die ?iezemente. Diese Regelsignale werden in einem Digital/Analog-Wandler 2 digital-/analog-gewan delt und zwei Schaltern 3 und 4 zugef·uhrt. Die ·Offnungs- und Schliesszeiten dieser Schalter sowie der Schalter 5 und 6 werden von den an den Ausg·angen C und D des Microcomputers 1 anliegenden Steuersignalen gesteuert. Der Schalter 3 ist immer dann geschlossen, wenn der am Piezoelement 1 befestigte Kopf im Bandeingriff steht.
Der Schalter 5 befindet sich w·ahrend dieser Zeitspanne in der Stellung b, so dass die am Ausgang des D/A-Wandlers 2 anliegende Regelspannung ·uber die Schalter 3 und 5 an das Piezoelement 1 weitergegeben wird und der am Piezoelement 1 befestigte Magnetkopf der durch die Regelspannung vorgegebenen Spur folgt.
Ist die Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 1 im Bandeingriff, dann befindet sich die Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 2 in ihrer Nichteingriffsphase. Diese Zeitspanne wird ausgenutzt, um dem Piezoelement 2 ·uber den Schalter 6, der sich
 hierbei in der Stellung b
befindet, eine abklingende rechteckf·ormige Spannung von einem vom
Microcomputer 1 gesteuerten Generator 7 zuzuf·uhren.
hierbei in der Stellung b
befindet, eine abklingende rechteckf·ormige Spannung von einem vom
Microcomputer 1 gesteuerten Generator 7 zuzuf·uhren.Damit wird eine eventuelle Restauslenkung des zugeharigen Magnetkopf es, die ihre Ursache in der Hysterese im Piezoelement 2 hat, vollst·andig beseitigt. Besonders wirkungsvoll ist gem·ass einem Merkmal der Erfindung die Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte des Piezoelementes dann, wenn die Frequenz der angelegten Rechteckspannung knapp unterhalb der mechanischen Resonanzfrequenz (ungef·ahr 1 kHz) des Piezoelementes liegt, also beispielsweise in der Gr·ossenordnung von 700 Hz.
Hat der Magnetkopf 1 die Spur zuende gelesen bzw.
geschrieben, -so findet eine vom Microcomputer gesteuerte Kopfumschaltung statt. Jetzt wird eine am Ausgang des D/A-Wandlers 2 anliegende analoge Regelspannung durch den geschlossenen Schalter 4 und den Schalter 6, der sich in der Stell
 ung a befindet, an das Piezoelement 2 weitergeleitet,
so dass der am Piezoelement 2 befestigte Magnetkopf der ihm durch die
Regelspannung aufgepr·agten Spur folgt.
ung a befindet, an das Piezoelement 2 weitergeleitet,
so dass der am Piezoelement 2 befestigte Magnetkopf der ihm durch die
Regelspannung aufgepr·agten Spur folgt.Der Schalter 3 ist in dieser Phase ge·offnet. Gleichzeitig dazu wird dem Piezoelement 1 ·uber den Schalter 5, der sich in dieser Phase in der Stellung a befindet, eine abklingende Rechteckspannung von einem vom Microcomputer 1 gesteuerten Generator 8 zur vollst·andigen Beseitigung des Hystereseeffektes des Piezoelementes 1 zugef·uhrt, die eine eventuelle Restauslenkung der Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 1 beseitigt, so dass der Magnetkopf 1 am Beginn seines n·achsten Bandeingriffes an der richtigen Stelle steht.
Figur 2 gibt einen ·Uberblick ·uber
die an die Piezoelemente 1 und 2 angelegten Spannungen. Dabei entsprechen die Zeitintervalle [ t1, t2 ] , [ t3 > t4 ] > [ t5, t6 ] , den Bandeingriffsphasen der Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 1 und den Nichteingriffsphasen der Kopf-Piezoelement Einheit 2 und die Zeitintervalle [ t2, t3 ] [ t4, t5 [ t6, t7 ] , den Bandeingriffsphasen der Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 2 und den Nichteingriffsphasen der Kopf-Piezoelement-Einheit 1.
Die obengenannten Zeitintervalle, die f·ur die Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte der Piezoelemente 1 bzw.
2 zur Verf·ugung stehen, liegen bei Verwendung von zwei um 180 Grad versetzten Magnetk·opfen im Normalbetrieb bei 20 msec. Es hat sich ·uberraschenderweise gezeigt, dass eine Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte der Piezoelemente besonders wirkungsvoll ist, wenn die-Frequenz der Spannung zur Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte knapp unterhalb der mechanischen Resonanzfrequenz der Piezoelemente gew·ahlt wird, die in der Gr·ossenordnung von 900 - 1200 Hz liegt, und eine abklingende Rechteckspannung verwendet wird. Bei der Wahl der Frequenz muss lediglich darauf geachtet werden, dass keine st·orenden Resonanzerscheinungen auftreten, d. h. dass die Frequenz nicht zu nahe bei der mechanischen Resonanzfrequenz der Piezoelemente liegt.

W·ahlt man beispielswelse 700 Hz, dann betr·agt die Dauer einer Schwingung 1,4 msec. In der zur Verf·u gung stehenden Zeitspanne von 20 msec. w·are somit eine Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte mit ca. 14 Schwingungen m·oglich.
Der exakte Verlauf des Abklingvorganges (Verlauf der Einh·ullenden der abklingenden Rechteckspannung) richtet sich nach den physikalischen Eigenschaften des jeweils verwendeten Aktuatormaterials. Es ist in jedem Fall darauf zu achten, dass die Amplitude der letzten Rechteckschwingung hinreichend klein gew·ahlt wird.
Bei einigen neueren Entwicklungen im Videobereich (z. B. Kamerarecorder) werden immer kleinere Kopfr·ader verwendet und es liegt eine ·Uberumschlingung des Magnetbandes um das Kopfrad vor. Demzufolge werden die Nichteintauchphasen der Kopf-Piezoelement Einheiten und damit die zum Beseitigen der Hystereseeffekte zur Verf·ugung stehenden Zeitintervalle kleiner. Auch werden bei einigen neueren Trends die Zeitintervalle, in denen Spannungen (insbesondere Gleichspannungn) an den Piezoelementen anliegen, und/oder die Amplituden der an die Piezoelemente angelegten Spannungen gr·osser.
Dies kann eine Desensibilisierung der Piezoelemente gegen·uber der angelegten Spannung zur Folge haben, d. h. die Piezoelemente k·onnen dann, wenn ·uber einen l·angeren Zeitraum eine hohe Gleichspannung--an ihnen anliegt-, gegen·ubn der angelegten Spannung unempfindlich werden, so dass Spurfehler entstehen. Auch dieser Nachteil wird durch eine Beseitigung der Hystereseeffekte nach der vorliegenden Erfindung in vorteilhafter Weise vermieden.
 out any guard band therebetween by means of two video heads which
rotate in a common plane with different azimuth angles. During still
picture recording, two adjacent slant tracks are continuously or
repetitively scanned by two rotating video hands which have different
azimuth angles with one head displaced axially by one slant track width
with respect to the other. During still mode reproduction, the two
adjacent slant tracks are continuously scanned by mechanically
deflecting the two rotating video heads by way of plungers following a
ring.
out any guard band therebetween by means of two video heads which
rotate in a common plane with different azimuth angles. During still
picture recording, two adjacent slant tracks are continuously or
repetitively scanned by two rotating video hands which have different
azimuth angles with one head displaced axially by one slant track width
with respect to the other. During still mode reproduction, the two
adjacent slant tracks are continuously scanned by mechanically
deflecting the two rotating video heads by way of plungers following a
ring.  1. A device for the
recording, reproduction, and distortion-free reproduction of slant
tracks recorded on magnetic video tape without any intermediate spacing
between adjacent tracks, said device comprising: a drum; two video heads
mounted in said drum and adapted to rotate in a common plane with
different azimuth angles; a pair of spring leaves, each of said heads
being mounted to one of said springs; a pair of plungers, each plunger
having one end engaging one of said springs and an opposite end; and an
axially adjustable ring mounted in said drum, said ring having an upper
surface which rises linearly for half the width of a slant track about
half its circumference and declines linearly over the remaining half of
its circumference, said ring being adjustable between a first position
out of contact with said plungers and a second position wherein said
plungers' opposite ends engage said ring upper surface; and one of said
plungers is shorter than the other of said plungers by the width of a
slant track.
1. A device for the
recording, reproduction, and distortion-free reproduction of slant
tracks recorded on magnetic video tape without any intermediate spacing
between adjacent tracks, said device comprising: a drum; two video heads
mounted in said drum and adapted to rotate in a common plane with
different azimuth angles; a pair of spring leaves, each of said heads
being mounted to one of said springs; a pair of plungers, each plunger
having one end engaging one of said springs and an opposite end; and an
axially adjustable ring mounted in said drum, said ring having an upper
surface which rises linearly for half the width of a slant track about
half its circumference and declines linearly over the remaining half of
its circumference, said ring being adjustable between a first position
out of contact with said plungers and a second position wherein said
plungers' opposite ends engage said ring upper surface; and one of said
plungers is shorter than the other of said plungers by the width of a
slant track. The present invention relates to video recording and in particular to reproducing still pictures recorded along slant tracks on magnetic video tape.
 When
reproducing still pictures recorded on slant tracks on magnetic tape it
is common practice to repeatedly scan the same slant track with the
rotating head or heads. This is particularly true for the widely used
devices wherein a field is recorded per slant track with two 180° offset
video heads. The two video heads scan the same slant track in sequence
and repeatedly. However, the signal-to-noise ratio with such devices is
reduced when the magnetic tape is idle as compared to when the tape is
moving since the scanning device of the video heads is not in conformity
with the recorded tracks. This is illustrated in FIG. 1 wherein tracks 2
and 3 depict the tracks recorded (or scanned) by a video head when the
tape is in motion and track 4 depicts a track recorded (or scanned) when
the tape is stopped.
When
reproducing still pictures recorded on slant tracks on magnetic tape it
is common practice to repeatedly scan the same slant track with the
rotating head or heads. This is particularly true for the widely used
devices wherein a field is recorded per slant track with two 180° offset
video heads. The two video heads scan the same slant track in sequence
and repeatedly. However, the signal-to-noise ratio with such devices is
reduced when the magnetic tape is idle as compared to when the tape is
moving since the scanning device of the video heads is not in conformity
with the recorded tracks. This is illustrated in FIG. 1 wherein tracks 2
and 3 depict the tracks recorded (or scanned) by a video head when the
tape is in motion and track 4 depicts a track recorded (or scanned) when
the tape is stopped. Heretofore, several proposals to eliminate the error resulting from the above have been proposed. For example, the angle of inclination of the total slant track cylinder may be changed so that the video heads follow the recorded tracks 2 and 3, even when the tape is idle. This is suggested in U.S. Pat. No. 3,375,331. French Pat. No. 2,107,066 suggests the vertical adjustment of the tape feed at the slant track cylinder. IBM Technical Disclosure Bulletin, June 1969, pages 33/34 suggests reciprocal movement of the video heads axially during each rotation of the head. Unfortunately, none of the above can be employed if for tape saving purposes, the slant tracks are recorded immediately adjacent to each other without any guard band and if they are recorded with different azimuth angles in order to eliminate cross talk. For example, a known device uses two video heads for recording and reproducing, wherein the azimuth angle of the gap of the one video head is 15° in clockwise direction and the azimuth angle of the gap of the other video head is 15° in counterclockwise direction. With this embodiment it is impossible to obtain a distortion-free still picture recording by means of repeated scanning of the same track, even if one of the above mentioned means for compensating for the differing angle between the scanning direction of the heads and the inclination of the recorded track is used.
In view of the above, it is an object of the present invention to provide a method to permit distortion-free still picture reproduction with such slant track devices, wherein adjacent slant tracks are recorded and scanned without a guard band therebetween and with different azimuth angles.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
 The
above and other beneficial objects are attained in accordance with the
present invention by providing a method for the distortion-free
reproduction of slant track magnetic video tape wherein adjacent tracks,
each containing a field, are recorded and scanned without any guard
band therebetween by means of two video heads which rotate in a common
plane with different azimuth angles. One of the video heads is displaced
axially with respect to the other head by a distance equal to one slant
track width of the magnetic tape.
The
above and other beneficial objects are attained in accordance with the
present invention by providing a method for the distortion-free
reproduction of slant track magnetic video tape wherein adjacent tracks,
each containing a field, are recorded and scanned without any guard
band therebetween by means of two video heads which rotate in a common
plane with different azimuth angles. One of the video heads is displaced
axially with respect to the other head by a distance equal to one slant
track width of the magnetic tape.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the accompanying drawings:
FIG. 1 is a plan view of a length of magnetic tape having slant tracks immediately adjacent to one another recorded thereon;
FIG. 2 is a simplified schematic drawing of a mounting arrangement for video heads in accordance with the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a wind up of the ring of FIG. 2; that is, FIG. 3 sets forth the height of ring 13 as a function of angular displacement proceeding for a full 360° about the ring;
FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a circuit for carrying out the present invention electronically; and,
FIG. 5 is a waveform diagram of various outputs of the circuit of FIG. 4.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
In accordance with the present invention, an arrangement is provided to compensate for the different angles o
f the slant track when the tape is idle or moving. Reference is made to FIG. 2 wherein a first embodiment of the invention is depicted schematically. Two video heads 5 and 6 which differ in their azimuth angles are mounted on the head wheel 7 on spring plates 8 and 9. The video heads 5 and 6 are adjusted by screws 10 and 11 to their desired position, that is, so that they lie in a common rotational plane for the normal operation. A ring 13 is provided in the lower stationary slant track cylinder 12. Ring 13 can be shifted from the solid line position of FIG. 2 to the position of FIG. 2 as shown in the dotted lines, when the device is switched from normal picture reproduction to still picture reproduction. The ring 13 is divided, as shown in FIG. 3, so that its upper edge rises linearly through half its circumference. The amount of change, which is denoted by the letter "X" is equal to the width of a slant track on the magnetic tape. Plungers 14 and 15 engage the upper edges of ring 13. The distance "X" corresponds to an axial displacement of one track width taking into consideration the lever transmission on springs 8 and 9. Plunger 15 is shorter by the distance X than plunger 14. As a result, the video head 5 is displaced with respect to video head 6 by a complete track width when the ring 13 is displaced into the position indicated by the dotted lines. When rotating the head wheel 7 both video heads move axially in accordance with the upper edge of ring 13 and thereby follow the recorded tracks 2 and 3 of FIG. 1.
A circuit for carrying out the inventive method with purely electronic means is shown in FIG. 4. In this embodiment the axial adjustment of the one video head by one track width
and the subsequent axial guiding of both video heads in accordance with the recorded tracks is carried out in a commonly known manner wherein the video heads are mounted on electromechanical transducers, for example, piezoceramic elements. The control voltages for the piezoceramic must be obtained from the scanned video signals. Accordingly, the tracks must be provided with suitable signals which, on the one hand should not interfere with the chrominance signals, and on the other hand must be readable for a video head with the "wrong" azimuth angle. For these reasons only very low frequencies are used for the signal frequencies. The frequencies should be beneath the chrominance subcarrier.
In accordance with this embodiment of the invention, synchronizing pulses of the video signal are applied to the terminal 16 (see FIG. 4) and are separated in separator 17 and fed to a filter 18 which supplies constant line pulses. A voltage controlled oscillator 19 oscillates at a median frequency of, for example, 16 times line frequency, and synchronizes the line pulse received from filter 18 across the dividers 20, 21 and 22 through phase comparator 23. A further divider 24 is coupled to the inverting output of 20. The inverted and noninverted outputs of 21 and 24 are fed to a multiplexer 25 which multiplexes the outputs by approximately 90° with respect to each other in the sequence of D1, D2, D3 and D4 as shown in FIG. 5.
Vertical blanking pulses received from separator 17 are filtered in the filter device 26 (which separates the ver
tical signal) and are converted to regular frame signals in 27. The frame signals are fed to the multiplexer 25 (input A) and are also fed to divider 28, the output of which is also fed to the multiplexer (input B).
Multiplexer 25 operates as a quadruple converter and switches the D-voltages in series in accordance with logical orders from its A and B inputs. This is shown schematically in FIG. 5. The output voltage of multiplexer 25 is filtered in filter 29 and fed to the center top of switch 30. This voltage may then be fed to a terminal 31 through switch 30 and from there the output voltage is added to the frequency modulated video signal before recordation. Since each halfwave of voltage A corresponds to a field and thereby to a slant track, a voltage of quadruple line frequency is superimposed to the frequency modulated video signal and the phase of the superimposed signal changes from slant track to slant track by about 90°. Simultaneously, the divided frame pulses in 28 are fed to a pulse shaper 32 wherein they are converted as shown in FIG. 5 in such a manner that when they are added to the video signal across terminal 33, one or a plurality of follow up equalizing pulses in the vertical signal of the first field of every second frame is blanked out. In this manner each slant track is coded by virtue of the phase of the D-voltage which superimposes the frequency modulated video signal and the start of each second frame by gating the follow up equalizing pulses. The frequency of the code signals is lower than the frequency ranges for chrominance and brightness and is locked to the line frequency.
 During the reproduction of a still picture, switch 30
is positioned with its center tap connecting with terminal W, switch 34
is closed and the scanned demodulated video signal is at terminal 16.
The scanned frequency modulated video signal from which the code
frequency is filtered out through band pass filter 36, is applied at
terminal 35 and is fed to a phase comparator 38 through limiter 37. The
vertical signals which are present at output 26 are tested in pulse
comparator 39 by means of a time circuit to determine if follow up
equalizing pulses are gated. If so, a reset (flip-flop) signal is fed to
divider 28, so that in accordance with the sketch in FIG. 5 only phases
D1 and D2 are discharged from the multiplexer 25
and fed to the comparator 38. The error signal of comparator 38 controls
an amplifier 40, the output of which is fed to a terminal 42 across a
switch 41. The electro-mechanical converters (which comprise, for
example, piezoceramic elements which are not shown) are coupled to the
terminal and the video heads are mounted to the piezoceramic. During
recording, switch 41 is in position A and the electromechanical
converters are fed with a constant bias, so that they rotate in a common
plane.
During the reproduction of a still picture, switch 30
is positioned with its center tap connecting with terminal W, switch 34
is closed and the scanned demodulated video signal is at terminal 16.
The scanned frequency modulated video signal from which the code
frequency is filtered out through band pass filter 36, is applied at
terminal 35 and is fed to a phase comparator 38 through limiter 37. The
vertical signals which are present at output 26 are tested in pulse
comparator 39 by means of a time circuit to determine if follow up
equalizing pulses are gated. If so, a reset (flip-flop) signal is fed to
divider 28, so that in accordance with the sketch in FIG. 5 only phases
D1 and D2 are discharged from the multiplexer 25
and fed to the comparator 38. The error signal of comparator 38 controls
an amplifier 40, the output of which is fed to a terminal 42 across a
switch 41. The electro-mechanical converters (which comprise, for
example, piezoceramic elements which are not shown) are coupled to the
terminal and the video heads are mounted to the piezoceramic. During
recording, switch 41 is in position A and the electromechanical
converters are fed with a constant bias, so that they rotate in a common
plane.




























0 commenti:
Post a Comment
The most important thing to remember about the Comment rules is this: The determination of whether any comment is in compliance is at the sole discretion of this blog’s owner. Fair people are getting fair reply. Spam and useless crap and shitty comments / scrapers / observations goes all directly to My Private HELL without even appearing in public !!!
Requiring blog comments to obey well-defined rules does not infringe on the free speech of commenters.
Resisting the tide of post-modernity may be difficult, but I will attempt it anyway.
Your choice.........Live or DIE.
That indeed is where your liberty lies.
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.